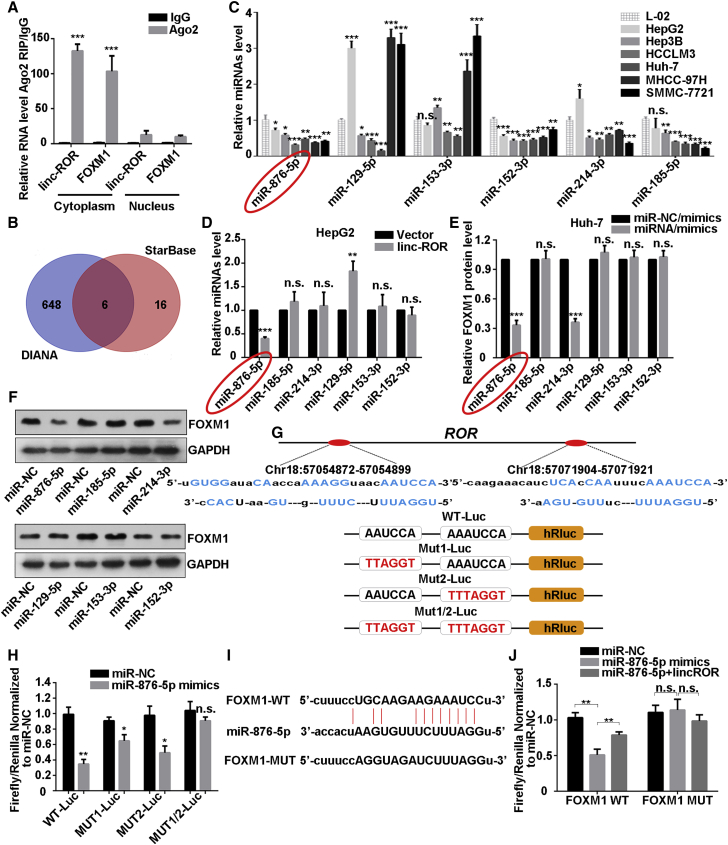
Figure 3.
LINC-ROR Acts as a Competing Endogenous RNA for miR-876-5p to Regulate FOXM1 Expression
(A) RIP experiments revealed that LINC-ROR and FOXM1 mRNA coexisted in the anti-Ago2 complex in the cell cytoplasm. IgG was used as the negative control. (B) A Venn diagram shows the overlapping miRNAs that are predicted to bind with both LINC-ROR and the 3′ UTR of FOXM1 mRNA. (C) The expression levels of the miRNAs were detected with quantitative real-time PCR in a normal liver cell line and six HCC cell lines. (D) The expression levels of the six miRNAs were measured individually by quantitative real-time PCR methods in LINC-ROR-transfected HepG2 cells. (E) Quantitative real-time PCR and (F) western blot analysis of FOXM1 expression after all six miRNA mimics were introduced. (G) Binding sequences of LINC-ROR and miR-876-5p based on bioinformatics analysis and schematic constructions of WT-Luc (LINC-ROR 3′ partial region), Mut1-Luc, Mut2-Luc, and Mut1/2-Luc. (H) Dual-luciferase reporter assays were performed to examine the potential combination of LINC-ROR and miR-876-5p. (I) WT and mutant binding sites of miR-876-5p and 3′ UTR of FOXM1 mRNA from StarBase (http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/). (J) Dual-luciferase reporter assays were conducted to confirm the association of FOXM1 and LINC-ROR or miR-876-5p and FOXM1. All data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. The p values represent comparisons between groups (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; ns, not significant).