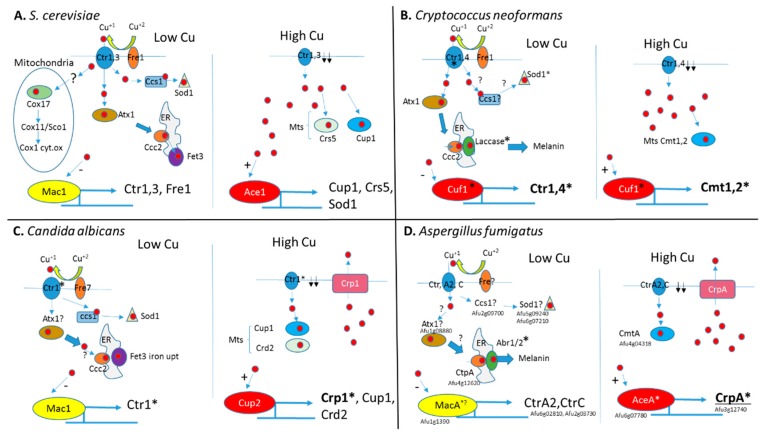
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of copper homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida albicans, and A. fumigatus. (A) In S. cerevisiae, under low Cu+, Fre1 reduces Cu+2 to Cu+ (red circles) for uptake by transporters Ctr1 and Ctr3. Inside the cell, Cu+ is bound by chaperone proteins Cox17, Atx1, and Ccs1 that transport Cu+ to the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase Cox1, ER-localized Fet3 ferric reductase, and Sod1 superoxide dismutase, respectively. Low intracellular Cu+ levels are sensed by transcription factor Mac1 to activate genes encoding the copper transporters Ctr1, Ctr3, and Fre1 reductase. High intracellular Cu+ levels are sensed by Ace1 transcription factor to activate the genes encoding metallothioneins (Mts) Cup1 and Crs5 and superoxide dismutase Sod1. Cup1 and Crs5 bind excess intracellular Cu+ and Sod1 oxidizes oxygen radicals formed under excess Cu+. High intracellular Cu+ levels also inhibit Mac1 activation to downregulate Ctr1 and Ctr3 expression. (B) In C. neoformans under low Cu+, Fre1 reduces Cu+2 to Cu+ (red circles) for uptake by transporters Ctr1 and Ctr4. Inside the cell, Cu+ is bound by chaperone proteins Atx1 and possibly a Ccs1 homolog. Atx1 transports Cu+ to the ER-localized laccase involved in melanin biosynthesis. A Ccs1 homolog is predicted to transport Cu+ to Sod1 superoxide dismutase. Low intracellular Cu+ levels are sensed by the transcription factor Cuf1 to activate the genes encoding the copper transporters Ctr1 and Ctr4. High intracellular Cu+ levels are also sensed by Cuf1 to activate the genes encoding metallothioneins (Mts) Cmt1 and Cmt2 to bind excess Cu+ and downregulate copper transporters Ctr1 and Ctr4. (C) In C. albicans under low Cu+, ferric reductase Fre7 reduces Cu+2 to Cu+ (red circles) for uptake by Cu+ transporter Ctr1. Inside the cell, Cu+ is bound by chaperone protein ccs1 that provides Cu+ to superoxide dismutase sod1. A putative Atx1 homolog is proposed to transfer Cu+ to the ER-Cu+ transporter Ccc2, providing copper for the Fet3 ferric reductase involved in iron uptake. Low intracellular Cu+ levels are sensed by transcription factor Mac1 to activate Ctr1 encoding copper transporters. High intracellular Cu+ levels are sensed by transcription factor Cup2 to activate the genes encoding Crp1 copper exporter, Cup1 and Crd2 metallothioneins to respectively remove or bind excess Cu+. (D) In A. fumigatus under low Cu+, an unknown ferric reductase (Fre?) reduces Cu+2 to Cu+ (red circles) for uptake by transporters CtrA2 and CtrC. Inside the cell, Cu+ presumably binds uncharacterized chaperone proteins homologous to yeast Atx1 and Ccs1. The ER-Cu+ transporter CtpA provides copper for the conidial laccases Abr1 and Abr2 that generate melanin. Low intracellular Cu+ levels are sensed by transcription factor MacA to activate genes encoding the copper transporters CtrA2 and CtrC. High intracellular Cu+ levels are sensed by AceA to activate CrpA encoding a copper exporter. Induced overexpression of the metallothionein CmtA also partially protects against Cu+ excess. A. fumigatus gene designations are provided. Genes whose deletion reduces virulence are marked by an asterisk *.