Figure 1.
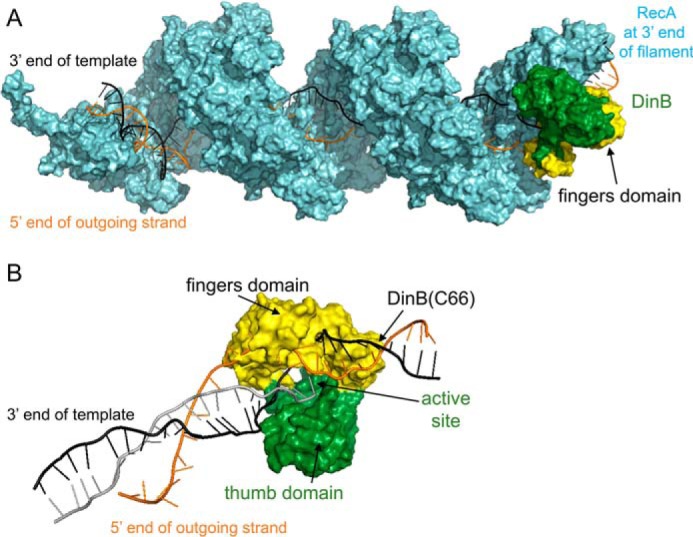
Molecular modeling of DinB in RecA-mediated strand exchange indicates the DinB fingers domain separates dsDNA. A, this model of RecA–DNA–DinB interaction represents the homologous recombination stage where strand exchange has taken place up to the 3′ extremity of the incoming strand. Interactions were modeled using structures and models as follows. The ssDNA (gray, largely obscured by RecA), template strand of dsDNA (black), displaced strand of dsDNA (orange), and RecA (cyan) were modeled using the PDB structure 3CMW (51) that had been extended by three turns (52) in a previous model (53). DinB (green and yellow) was modeled using the PDB structure 4IRC (43). The RecA nucleoprotein filament and DinB are shown interacting with the RecA molecule that lies at the 3′ end of the nucleoprotein filament. DinB and the RecA nucleoprotein filament were surface-rendered with PyMOL (42). The fingers domain of DinB is highlighted in yellow. B, DinB and DNA are shown without RecA to permit visualization of DinB's interaction with three DNA strands during strand exchange. Structures have been turned ∼180° about the horizontal axis with respect to A. DinB's fingers domains (yellow) appears to separate the template (black) and displaced (orange) strands of the dsDNA.
