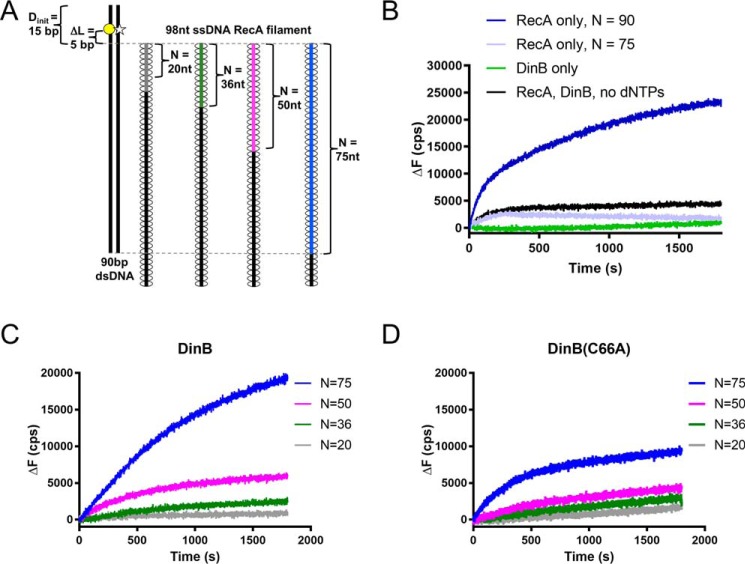
Figure 4.
Highly conserved fingers domain residue is important for DinB's activity during strand exchange. A, schematic shows experimental setup for RecA-dependent strand-exchange experiments. Fluorescently-labeled dsDNA (left) is mixed with each of a set of ssDNA RecA filaments (right). Each in the set of filaments contains a different length of homology (N) to the labeled dsDNA (signified by gray, green, magenta, and blue lines). In the dsDNA, the template strand is labeled with rhodamine (yellow circle), and the displaced strand is labeled with fluorescein (white star). These fluorophores are located 5 bp away from area of homology between dsDNA and ssDNA RecA filament (ΔL = 5 bp). The proximity of the rhodamine quenches fluorescein fluorescence until template and displaced strands are separated. Fluorescence increases when the ssDNA RecA filament invades the dsDNA, and DinB synthesizes DNA using the ssDNA filament as a primer. Five nucleotide insertions are needed to separate the displaced strand at the location of the fluorescent labels and relieve quenching. B, when only RecA or only DinB is mixed with the highest homology ssDNA RecA filament (N = 75, blue filament in A), the fluorescent labels are not efficiently separated, indicating that the dsDNA is still annealed at the location of the labels. When both proteins are present in the absence of dCTP, dGTP, and dTTP (dATP is present for nucleoprotein filament assembly), baseline fluorescence is observed. A RecA filament with full homology to the dsDNA (N = 90) is used to determine maximum possible fluorescence in the assay. C, DinB stabilizes strand exchange in a homology-dependent manner. As homology increases between the ssDNA RecA filament and the fluorescently-labeled dsDNA, DinB efficiently separates the dsDNA at the location of the fluorescent labels. This indicates that increased homology allows DinB to more efficiently stabilize strand-exchange products. D, DinB(C66A) stabilizes strand-exchange products, but it does so with less efficiency than the native enzyme. N indicates the length of homology between dsDNA and ssDNA filament; ΔL indicates the distance between region of homology on dsDNA and fluorescent label; Dinit indicates the distance between fluorescent label and closet end of dsDNA; ΔF indicates the change in fluorescence measured in counts/s with respect to the fluorescence at 0 s. Experiments were performed in triplicate with similar results. Representative data are shown.