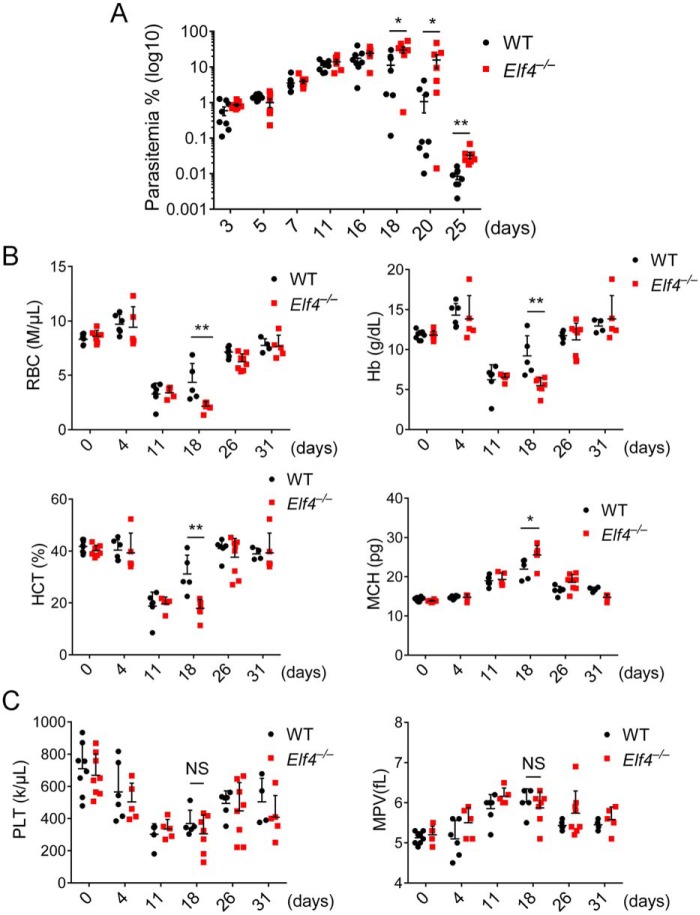
Figure 1.
Elf4-deficient mice suffer from severe malarial anemia. A, parasitemia of Elf4+/+ and Elf4−/− mice infected with GFP–P. yoelii 17XNL (1 × 105 infected red blood cells) on the indicated days after infection was assessed by analyzing the percentage of GFP-positive red blood cells (infected) via flow-cytometry. B, the severity of malarial anemia was assessed by detecting RBCs, Hb, HCT, and MCH levels on the indicated days after infection. C, the level of thrombocytopoiesis was assessed by peripheral platelet (PLT) counts and mean platelet volume (MPV). The data in A are means ± S.E. (n = 8 for Elf4+/+, n = 7 for Elf4−/−). The data in B and C are means ± S.D. All data are from three independent experiments; t test; *, p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; NS, not significant.