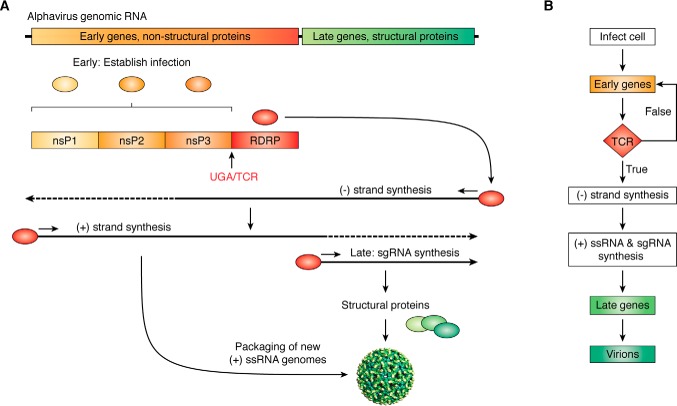
Figure 5.
Viruses use translational recoding to create integrated circuits and developmental programs. A, alphaviruses have (+)-ssRNA genomes harboring two open reading frames. Expression of early genes (nsP1–nsP3) occurs first; their function is to establish infection and hijack the cell. A TCR event produces the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. This initiates the second phase of the viral program, enabling synthesis of the (-)-ssRNA intermediate, new (+)-ssRNA genomes, and synthesis of the subgenomic RNA (sgRNA), which encodes the structural proteins to produce new virions. B, the alphavirus life cycle depicted as a programming flowchart.