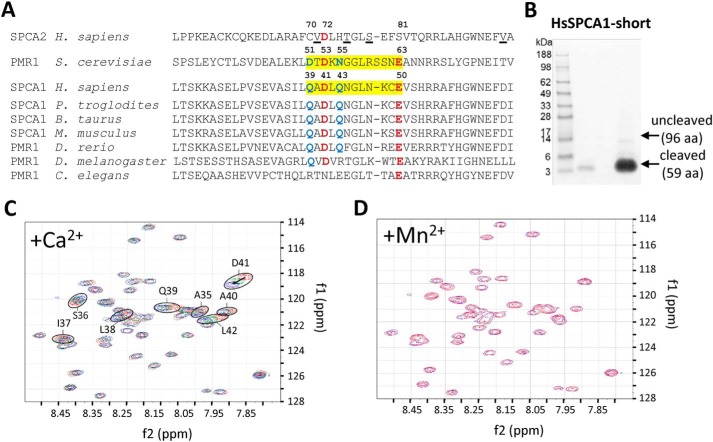
Figure 5.
Binding of Ca2+ to the N-terminal EF-hand–like motif in SPCA1a. A, MUSCLE alignment of part of the N-terminal sequences of yeast PMR1 (NP_011348.1), human SPCA1 (NP_001186110.1), and SPCA2 (B4E2Q0), with various animal SPCA1/PMR1 orthologues (XP_001146246.2; NP_786979.1; NP_001240760.1; XP_003200287.2; NP_730742.1; NP_001021862.1). The regions highlighted in yellow in yeast PMR1 and human SPCA1 correspond to the loop of the EF-hand–like motif. The critical residues that are identical (red) or conserved (blue) between yeast PMR1 and human SPCA1 are indicated with numbering. In SPCA2, the underlined residues interact with Orai1 during store-independent Ca2+ entry (11). B, Coomassie staining of purified N-terminal fragment of SPCA1a (including an N-terminal linker SPMGYRGSM followed by the human SPCA1a sequence Val-20 to Glu-67). C, the heteronuclear single quantum coherence spectra overlay of the SPCA1a N-terminal peptide purified from B in the presence of 0 (red), 4.65 (green), and 9 mm (blue) Ca2+ ions. Encircled residues with the indicated numbers were identified in close vicinity of a Ca2+ ion. D, overlay of heteronuclear single quantum coherence spectra before (blue) and after (red) further addition of Mn2+ after the Ca2+ titration.