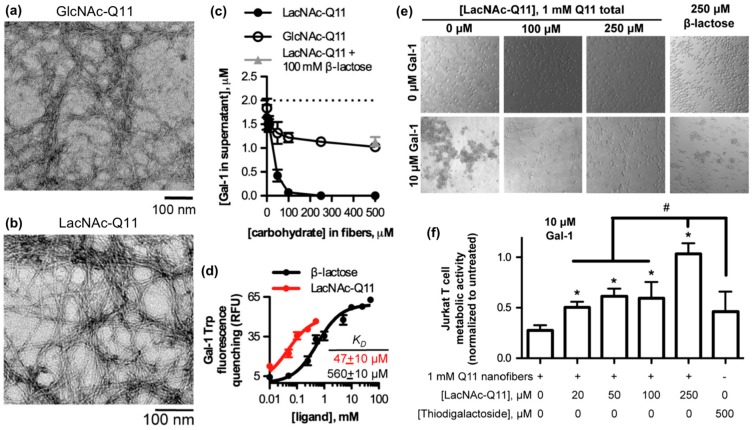
Figure 4.
Glycopeptide nanofibers that bind and inhibit galectin-1. (a) TEM of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc)-Q11 and (b) N-acetyllactosamine (LacNAc)-Q11 nanofibers assembled in aqueous buffer (pH 7.4). Images show similar fiber morphologies for GlcNAc-Q11 and LacNAc-Q11 fibers. (c) Binding of 2 μM Galectin-1 to LacNAc-Q11 (black circle) or GlcNAc-Q11 (hollow circle) nanofibers with 0–500 μM LacNAc or GlcNAc and (d) tryptophan fluorescence quenching of Galectin-1 by LacNAc-Q11 nanofibers or soluble β-lactose. Panel (c) also demonstrates inhibition of LacNAc-Q11 and Galectin-1 binding via β-lactose (triangle). (e) Bright-field photomicrographs of Jurkat T-cell agglutination and (f) metabolic activity of Jurkat T cells in culture media with or without Galectin-1 in the presence of Q11 nanofibers with different LacNAc content. LacNAc-Q11 nanofibers inhibited agglutination of Jurkat T cells induced by Galectin-1, whereas β-lactose was less effective. Likewise, LacNAc-Q11 nanofibers prevented the decrease in metabolic activity induced by Galectin-1, whereas thiodigalactoside was ineffective. * represents p < 0.05 compared to 0 μM LacNAc-Q11 or, # represents p < 0.05 compared to 250 μM LacNAc group, ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc. Adapted with permission from [94]. Copyright 2015, Springer US publishing.