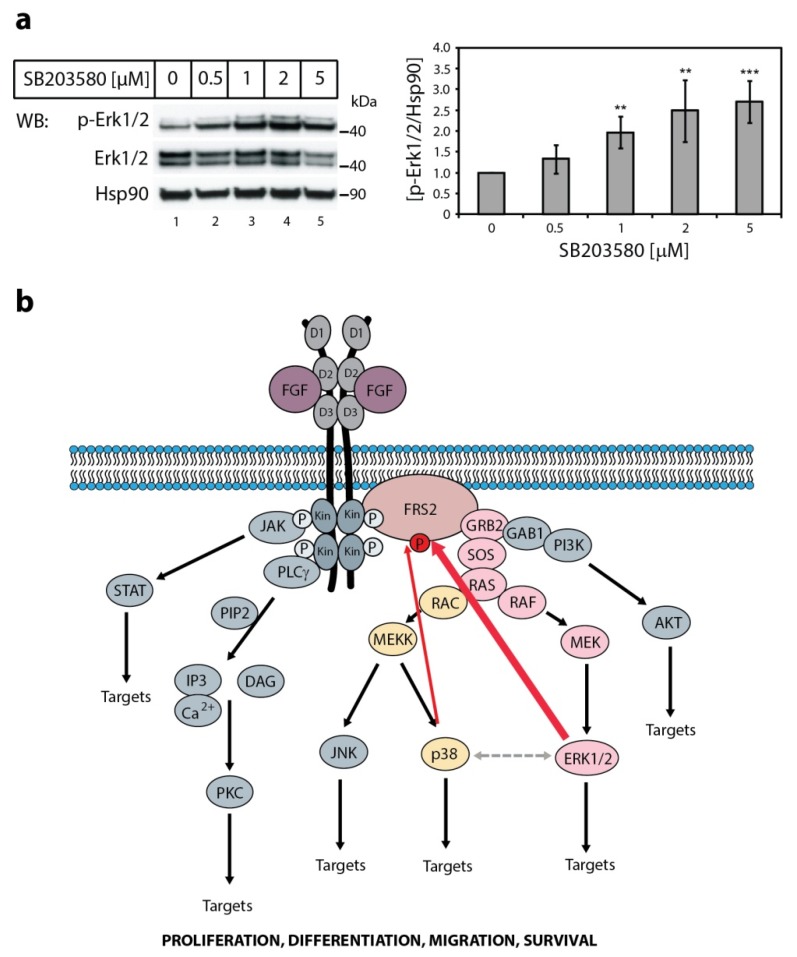
Figure 3.
The effect of p38 kinase activity on Erk1/2 activity and FGF1-induced signaling. (a) The effect of p38 specific inhibitor on Erk1/2 activity. Serum-starved NIH3T3 cells were treated with increasing concentration of the specific p38 kinase inhibitor SB203580 for 30 min. Then, the cells were lysed and the cellular material was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using the following antibodies: anti-phospho-Erk1/2 (p-Erk1/2), anti-Erk1/2, and anti-Hsp90 antibodies as a loading control. A representative experiment is shown, n = 4. The graph presents quantification of bands corresponding to phospho-Erk1/2 (p-Erk1/2) normalized to loading control (Hsp90) and expressed as a fold of change in comparison with untreated control. Data are means ± SD of four independent experiments; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. (b) Schematic representation of synergistic effect of p38 and Erk1/2 in the downregulation of FGF1-induced signaling through FRS2. FGF1-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of FGFR1 leads to the activation of FRS2 followed by GRB2/SOS-mediated activation of RAS and MAP kinases (Erk1/2 and p38). Activated Erks are supported by p38 in phosphorylation of FRS2 (red arrows), constituting a negative feedback loop that results in reduced tyrosine phosphorylation of FRS2 and consequent attenuation of FGFR signaling. Grey dashed line represents functional cross-talk between Erks and p38.