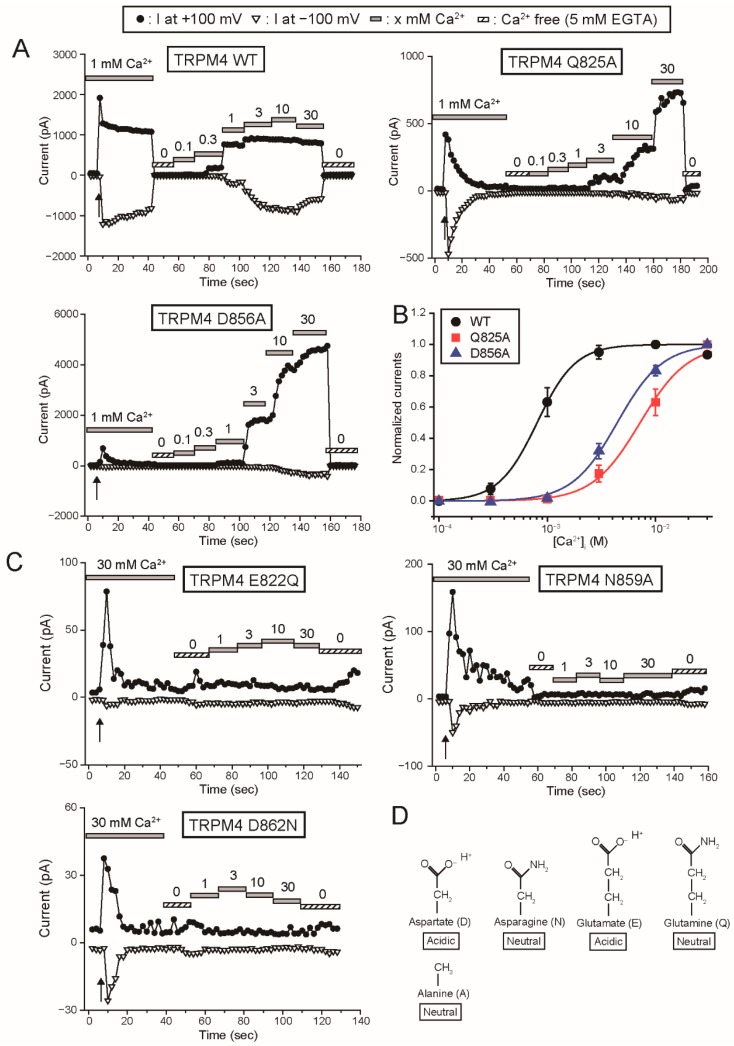
Figure 2.
Mutations of the amino acid residues of the proposed Ca2+-binding site of rTRPM4 reduced the Ca2+-sensitivity. (A) Typical time courses of the changes in the currents at +100 mV (filled circles) and −100 mV (open inverted triangles) of wild-type (WT) rTRPM4, Q825A and D856A. After the current amplitudes became almost steady in the presence of 1 mM intracellular Ca2+ (Ca2+i), Ca2+i concentrations ([Ca2+]i) were varied from 0 mM (chelated with 5 mM EGTA) to 30 mM. Arrows indicate the time of the patch excision. (B) Concentration-response curves (CRCs) for the effect of Ca2+ on WT TRPM4 (black circles), Q825A (red squares, and D856A (blue triangles). Current amplitudes at +100 mV were used for analyses. The shifts of CRCs by the mutations seemed to be underestimated, because the CRCs were drawn on the assumption that the current amplitudes at 30 mM Ca2+i were maximal but their current amplitudes at 30 mM Ca2+i were actually not saturated. (n = 7 or 8, each). (C) Typical time courses of the currents at +100 mV (filled circles) and −100 mV (open inverted triangles) of E822Q, N859A and D862N. Patch membranes were excised in the presence of 30 mM Ca2+i. Similar results were obtained repeatedly (n = 6 each). (D) Chemical structures of side chains of the amino acid residues which were mutated in this study.