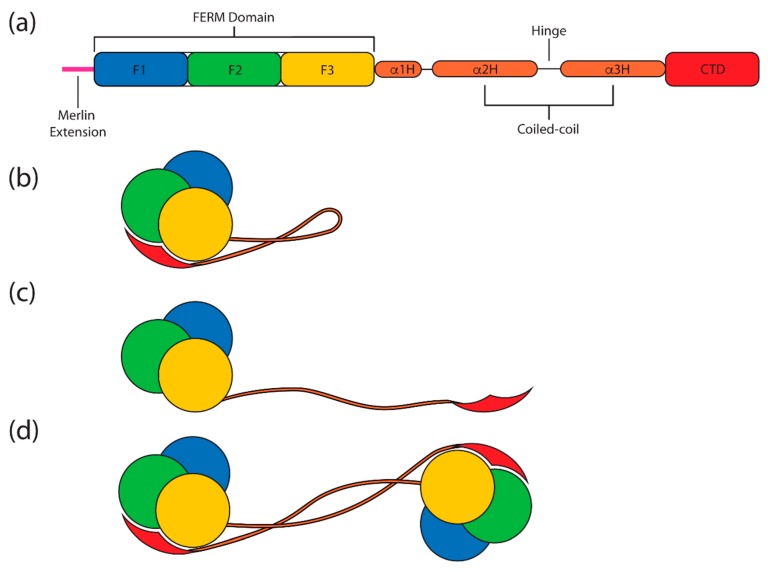
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of merlin-ERM (ezrin, radixin and moesin) protein domain structure and states. (a) The conserved domain structure of merlin-ERM proteins. The N-terminal FERM (band 4.1 protein, ezrin, radixin, moesin) domain comprises three subdomains, F1 (blue), F2 (green) and F3 (yellow). This is followed by a central helical domain comprising three α helices (orange), with the latter two, α2H and α3H, forming a coiled-coil in the monomer structure. At the C-terminus lies the largely α helical C-terminal domain (CTD, red). Note that merlin contains an N-terminal extension that is not seen in the ERM proteins (magenta). (b–d) show various states of merlin-ERM proteins. (b) represents the closed state monomer structure where the CTD and FERM domains form a globular structure with the α helical coiled-coil protruding. (c) represents the putative open state, where an extended “helical” domain separates the FERM and CTD domains. (d) shows the domain-swapped dimer state.