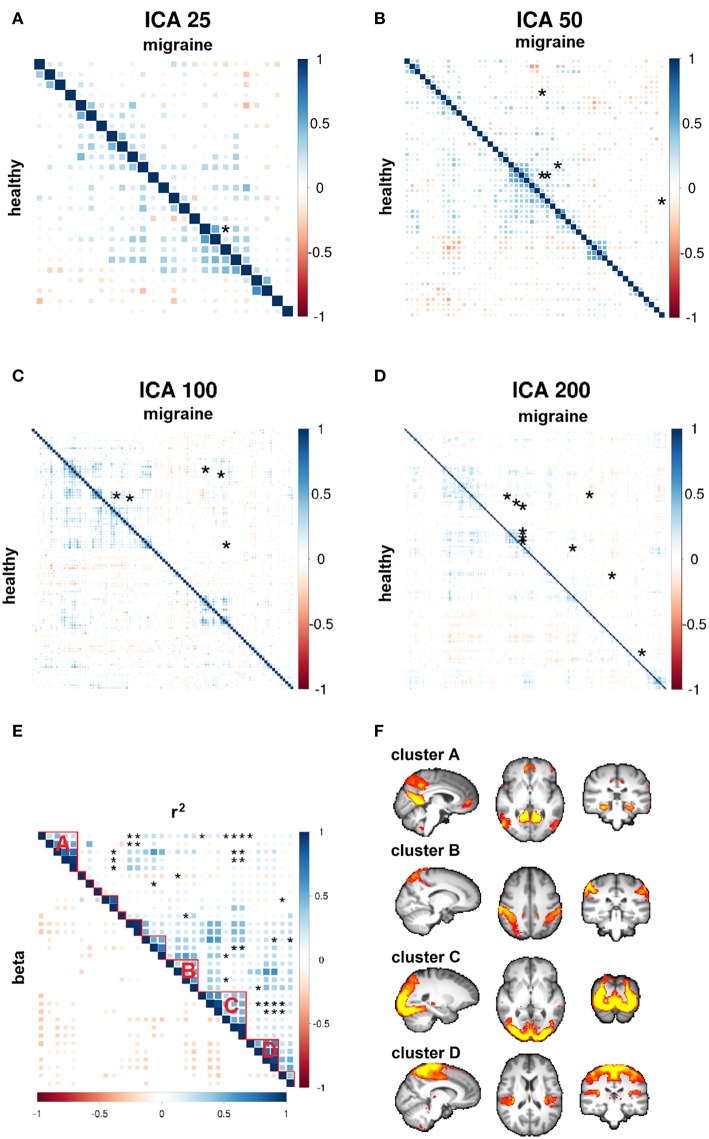
Figure 5.
Whole-brain functional connectivity differences. (A–D) Node-to-node correlation matrices of independent component analysis (ICA) time course are shown at various dimensions. Network edges with suggestive connectivity differences in the migraine vs. healthy group (p < 10−4) are marked by asterisks. These disease-related edges are pooled in a single cross-correlation matrix for the purpose of visualization (E, top triangle). Spatially localized clusters of connectivity disruption are observed in migraine patients (F). The sign of parameter estimates in regression models demonstrates generalized reduction of connectivity strength in migraine (E, bottom triangle; red-yellow: negative; blue: positive).