Figure 3.
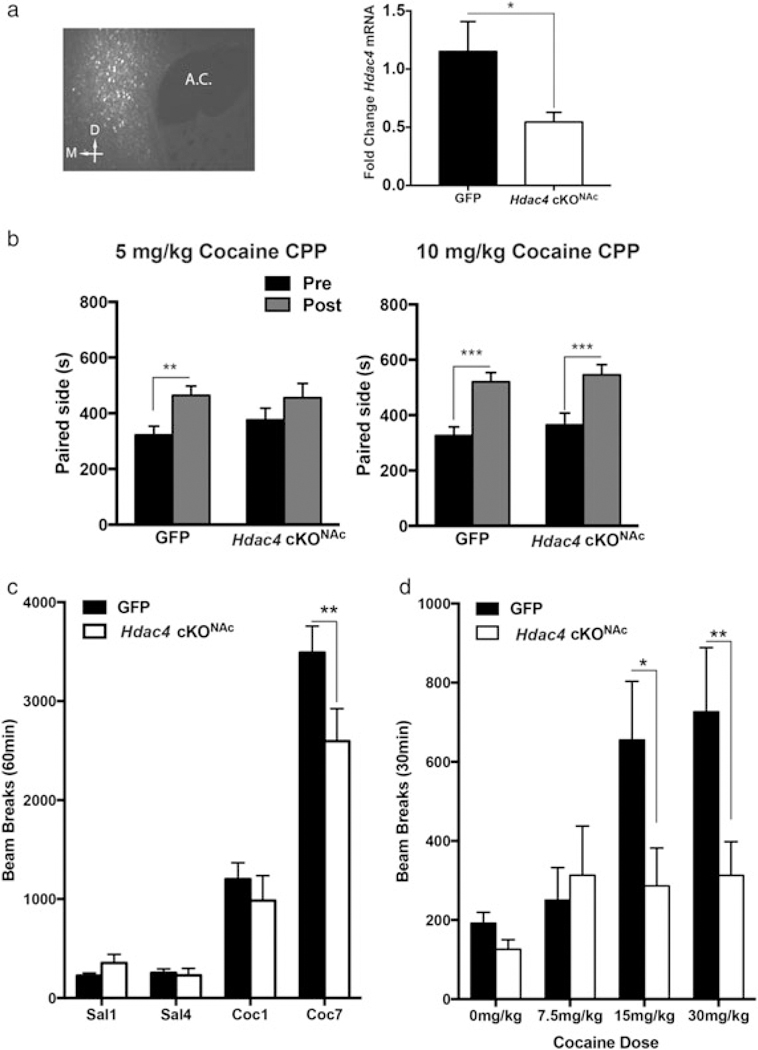
Loss of HDAC4 limits locomotor responses to acute and sensitizing regimens of cocaine. (a) Representative targeted expression in the NAc >21 days post-infection. Viral-mediated Cre expression significantly reduces HDAC4 mRNA. NAc punches from AAV-GFP or AAV-Cre-GFP Hdac4ffl/fl mice 3 weeks post-infection. HDAC4 mRNA is normalized to GAPDH and expressed as fold change compared with GFP control group (mean ± SEM, n = 6–7 NAc punches/condition). (b) Hdac4 NAc cKO disrupts low-dose (5 mg/kg) cocaine-conditioned place preference (left) but does not alter high-dose (10 mg/kg) cocaine CPP (right, mean ± SEM, n = 12–19 mice/condition). (c) Hdac4 NAc cKO decreases locomotor sensitization magnitude (mean ± SEM, n = 12–19 mice/condition). (d) Hdac4 NAc cKO decreases acute locomotor responses to cocaine (mean ± SEM, n = 8–10 mice/condition). Asterisks indicate significant difference from pre-test (b) or control group (a, c and d) in pairwise comparison, *P < 0.05,**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. AC, anterior commissure; D, dorsal; M, medial
