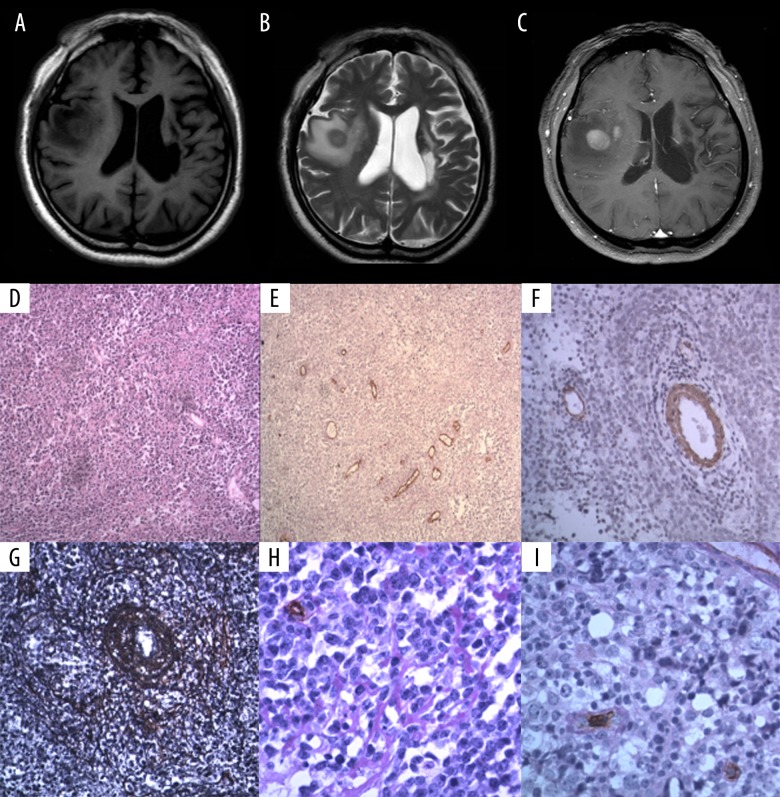
Figure 1.
A 56-year-old man with lymphoma involving right temporal lobe. Coronal brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and photomicrographs of the histology and immunohistochemistry. (A) Pre-contrast T1-weighted magnetic resonance image (MRI) of the brain. (B) Pre-contrast T2-weighted magnetic resonance image (MRI) of the brain. (C) Post-contrast T1-weighted magnetic resonance image (MRI) of the brain. (D) Photomicrograph of the histology of the cerebral lymphoma tissue shows large cells that are round or oval, with enlarged round or oval cell. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Magnification ×100. (E) Photomicrograph of the immunohistochemical staining of the vascular endothelial cells (blue arrow) for CD34 expression in the cerebral lymphoma tissue shows microvessel density (MVD)=33.66/mm2. Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS). Magnification ×100. (F) Photomicrograph of the immunohistochemical staining of smooth muscle cells for alpha smooth muscle actin (ASMA) expression in the cerebral lymphoma tissue shows that the number of mature vessels in the lymphoma was 8/mm2. Magnification ×200. (G) Photomicrograph of the silver staining for reticulin fibers in the cerebral lymphoma tissue shows the concentric perivascular reticular fiber network (white arrow). Magnification ×200. (H) Photomicrograph of the immunohistochemical staining of the vascular endothelial cells for CD34 expression in the cerebral lymphoma tissue combined with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) (red staining) shows the basal membrane (black arrow). Magnification ×400. (I) Photomicrograph of the immunohistochemical staining of the vascular endothelial cells for CD34 expression in the cerebral lymphoma tissue combined with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) (red staining) shows the basal membrane (yellow arrow). Magnification ×400.