Figure 2.
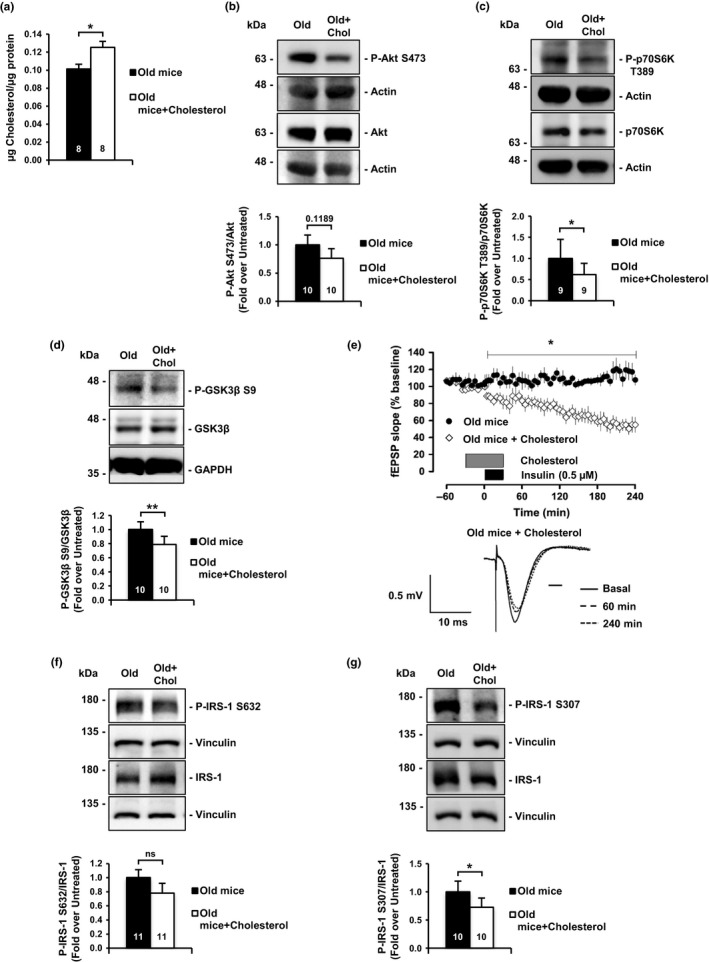
Ex vivo cholesterol replenishment in hippocampal slices of old mice restores insulin signaling. (a) Addition of cyclodextrin‐cholesterol (referred as MβCD‐Ch or Cholesterol) solution to old mice hippocampal slices induces a 20% increase in membrane cholesterol. (b, c) Cholesterol addition (as in a) reduces hyperactivated Akt and its downstream target p70S6K. (b) Detection of Akt Phospho‐Serine 473; (c) detection of p70S6K Phospho‐Threonine 389. (d) Cholesterol addition to old hippocampal slices reduces Phospho‐Serine 9 GSK3β inhibitory residue. (e) Addition of the cholesterol solution to hippocampal slices of old mice rescues the impairment of insulin‐LTD. Graphic showing insulin‐LTD induction in old mice slices (n = 7) and old mice slices incubated with MβCD‐Ch (n = 9). Black box indicates time of insulin application. Gray box indicates the time of MβCD‐Ch mix application. Representative analogue traces below were collected at the indicated time points. (f, g) Cholesterol replenishment decreases insulin resistance marks on IRS‐1 protein. (f) IRS‐1, Phospho‐Serine 632; (g) Phospho‐Serine 307. The value inside the bars indicates the number of independent experiments. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. t test for (a, b, d, g), Wilcoxon test for (c, f), one‐way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni's test for (e). The asterisks indicate the p values (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01)
