Figure 1.
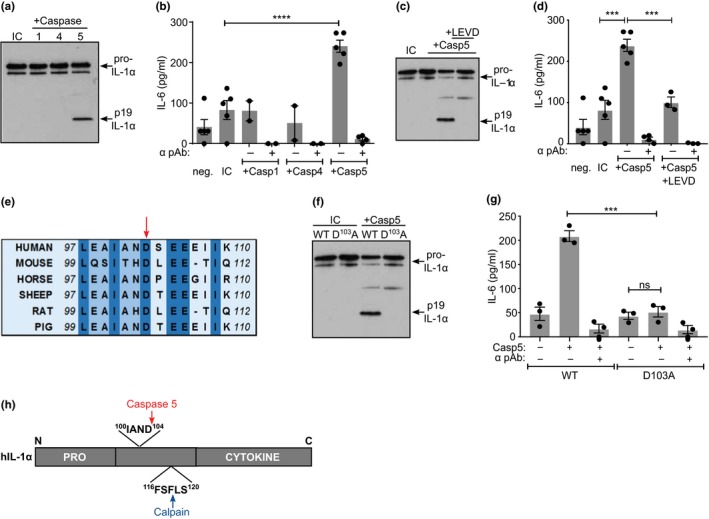
Caspase‐5 cleavage of human IL‐1α at a conserved site increases activity. (a) Western blot for IL‐1α after incubation of pro‐IL‐1α with active caspases, or alone (incubation control; IC). (b) IL‐1‐dependent IL‐6 production by HeLa cells treated with reaction products from pro‐IL‐1α incubated ± active caspases, ±neutralizing IL‐1α antibody (α pAb). (c, d) Western blot (c) and bioactivity (d) of IL‐1α after incubation ± caspase‐5, ±caspase inhibitor LEVD. (e) Multispecies IL‐1α protein alignment showing conserved aspartic acid residue (arrow). (f) Western blot for wild‐type (WT) or mutant D103A pro‐IL‐1α after incubation ± caspase‐5, or alone (IC). (g) IL‐1‐dependent IL‐6 production by HeLa cells treated with reaction products from WT or mutant pro‐IL‐1α incubated ± caspase‐5, ±neutralizing IL‐1α antibody (α pAb). (h) Pictograph showing position of cleavage sites in IL‐1α. Data represent mean ± SEM of n = 3 (g), n = 4 (b, d); p = **≤0.01, ***≤0.001, ****≤0.0001; ns = not significant
