Figure 1.
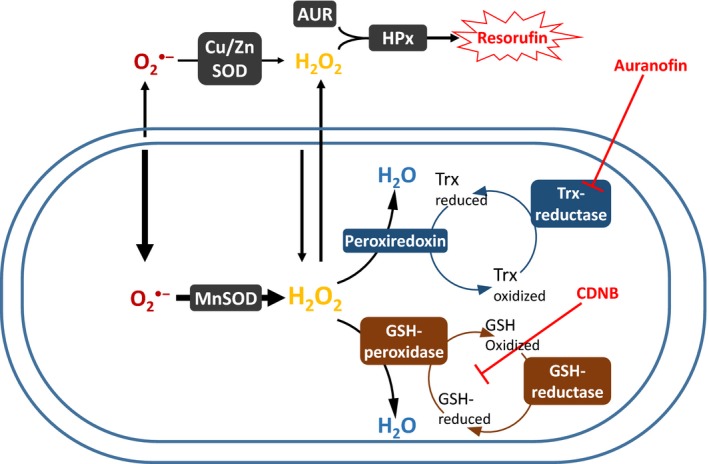
Metabolism of H2O2 during Horseradish peroxidase‐based efflux assays. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are generated on either side of the inner membrane, mostly under the form of superoxide (O2 •−) but also directly as H2O2. Superoxide released inside and outside the matrix will be converted into H2O2 by the Cu/ZnSOD and MnSOD, respectively. The proportion released inside is additive with the existing pool of H2O2, leading to two ultimate fates: (a) diffusion across membranes to reach the detection system, or (b) consumption by matrix‐based antioxidants pathways. The reductases of the GSH‐ and Trx‐dependent pathways are activated by provision of NADPH, when substrate is oxidized, and thus concomitantly with ROS formation. Inhibitors for the GSH (CDNB)‐ and Trx (auranofin)‐dependent pathways (also used in this study) are depicted in red
