Figure 3.
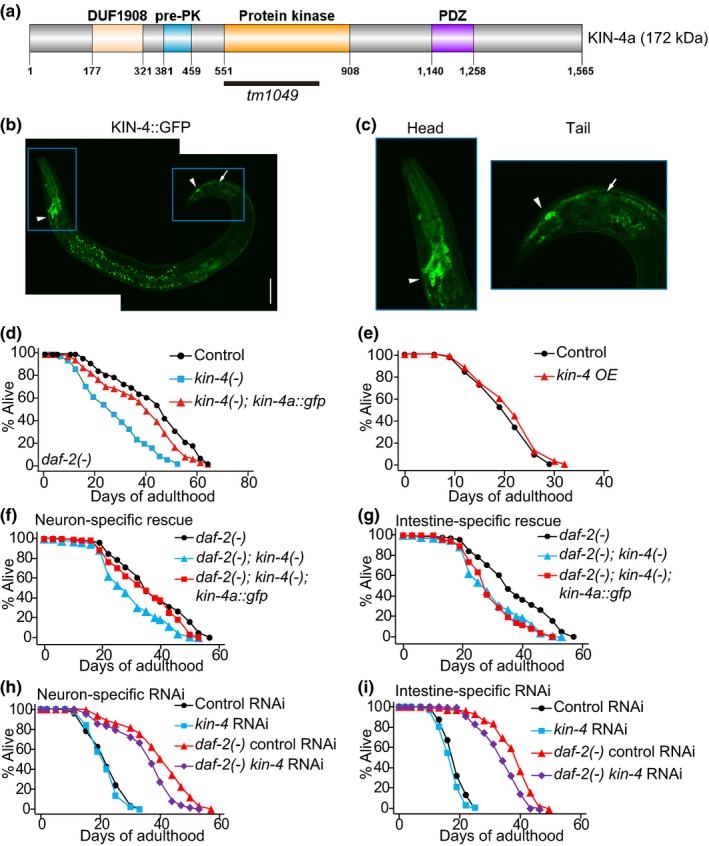
Neurons are crucial tissues for lifespan regulation by KIN‐4. (a) KIN‐4a is predicted to have 4 domains; DUF1908 whose function is not known, pre‐PK that is mainly found in MAST family kinases, protein kinase, and PDZ domains. The deleted part by kin‐4(tm1049) mutation is marked with a black solid line. (b, c) kin‐4::gfp transgene‐encoded protein (KIN‐4::GFP) was mainly expressed in head and tail (c) neurons (arrowheads) and dimly in the intestine (arrow). Scale bar indicates 50 μm. (d) KIN‐4a::GFP increased the shortened lifespan of daf‐2(e1370); kin‐4(tm1049) [daf‐2(−); kin‐4(−)] mutants. (e) kin‐4 transgenic worms did not display longevity. We also found that daf‐2 RNAi did not alter KIN‐4::GFP levels (Supporting information Figure S4d). See Supporting information Table S3 for experimental repeats and statistics. (f) Tissue‐specific promoter‐driven kin‐4a expression [daf‐2(−); kin‐4(−); kin‐4a::gfp] in neurons (daf‐2(e1370); kin‐4(tm1049); rgef‐1p::kin‐4a::gfp) prolonged the shortened lifespan of daf‐2(e1370); kin‐4(tm1049) [daf‐2(−); kin‐4(−)] mutants. (g) Transgenic expression of kin‐4a in the intestine (daf‐2(−); kin‐4(−); ges‐1p::kin‐4a::gfp) did not affect the decreased lifespan of daf‐2(−); kin‐4(−) mutants. (h) The long lifespan of daf‐2(−) mutants was decreased by neuron‐specific (sid‐1(pk3321); uIs69[myo‐2p::mCherry; unc‐119p::sid‐1]) kin‐4 RNAi treatment. (i) Knock‐down of kin‐4 in the intestine (rde‐1(ne213); kbIs7[nhx‐2p::rde‐1; rol‐6(su1006)]) significantly suppressed the long lifespan of daf‐2 mutants. See Supporting information Table S3 for experimental repeats and statistics
