Figure 3.
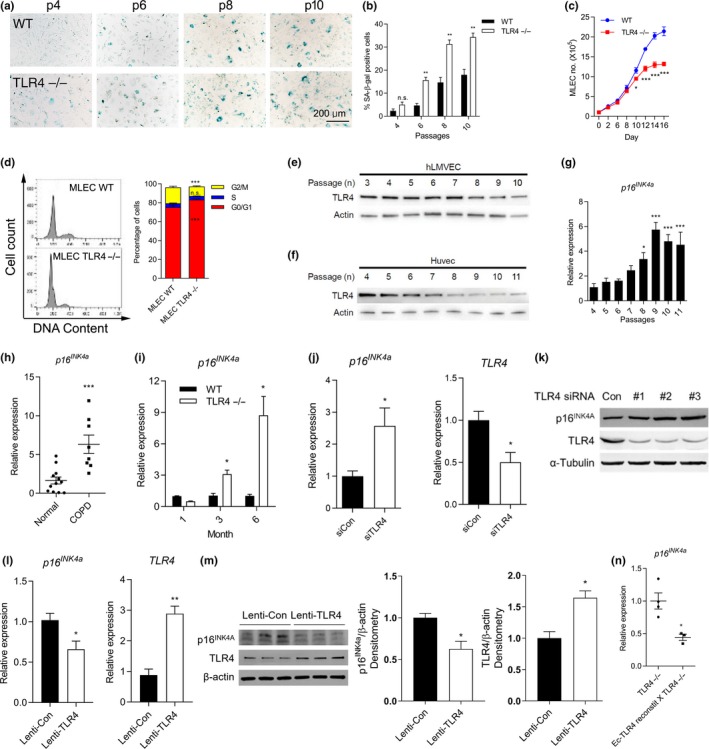
TLR4−/− induces cellular senescence in murine and human endothelial cells (Ec). (a) Representative images and (b) quantification of the senescence‐associated (SA)‐β‐gal activities in WT and TLR4−/− MLEC as passage numbers increase. Blue staining indicates SA‐β‐gal positive cells. **p < 0.01 vs. WT, n.s.: nonsignificant. (c) WT and TLR4−/− MLEC growth were observed over 16 days. (n = 3 in each group at different time points). *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 vs. WT. (d) FACS analysis of cell cycle for PI‐stained WT and TLR4−/− MLEC (n = 3 and n = 4, respectively). ***p < 0.001 vs. MLEC WT, n.s.: nonsignificant. TLR4 expression in (e) hLMVEC and (f) HUVEC at indicated passage numbers. (g) Expression of p16INK4a mRNA in HUVEC at indicated passage numbers. *p < 0.05, ***<0.001 vs. passage 4. (h) Expression of p16INK4a mRNA in lungs from normal and COPD subjects (n = 12 and 8, respectively). The mean ± SEM of ages are 59.5 ± 4.3 and 56.0 ± 1.8 in normal and COPD subjects, respectively. ***p < 0.001 vs. Normal. (i) p16INK4a mRNA expression in lungs at 1, 3, and 6 month of age from WT and TLR4−/− mice. (n = 3 per group) *p < 0.05 vs. age‐matched WT. (j) The mRNA and (k) protein expression of p16INK4a and TLR4 in control (siCon)‐ or TLR4‐siRNA (siTLR4)‐treated hLMVEC. *p < 0.05 vs. siCon. (l) The mRNA and (m) protein expression of p16INK4a and TLR4 in Lentiviral vector‐mediated hTLR4 overexpressed hLMVEC. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. Lenti‐Con. (n) p16INK4a mRNA expression in lung homogenates of TLR4−/− and Ec‐TLR4‐reconstit X TLR4−/− mice. (WT: n = 4, TLR4−/−: n = 3). *p < 0.05 vs. TLR4−/−.
