Figure 1.
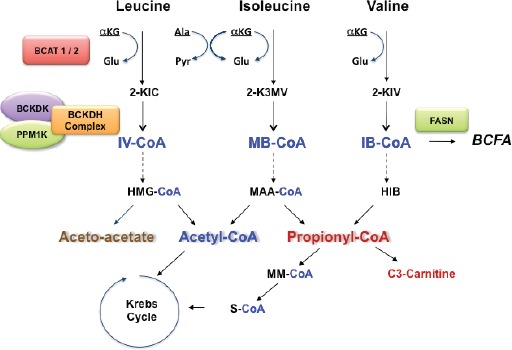
Major steps in the catabolism of BCAA. The first step in BCAA catabolism is determined by reversible transamination by the BCAT enzymes followed by irreversible oxidation by the BCKDH complex. Downstream metabolism is then independent for three amino acids, ketogenic for leucine and isoleucine (aceto acetate and acetyl Co-A) and glucogenic for valine with the formation of propionyl-CoA. Acetyl Co-A and succinyl-CoA enter then in the Krebs cycle for energy generation and gluconeogenesis or as precursors of lipogenesis and ketone bodies formation. Not indicated in the figure is AACS (acetoacetyl-CoA synthetase) located on Chr 12q24.31, which is a ketone body-utilizing ligase with a role in lipid synthesis through the non-oxidative pathway.
