Figure 2.
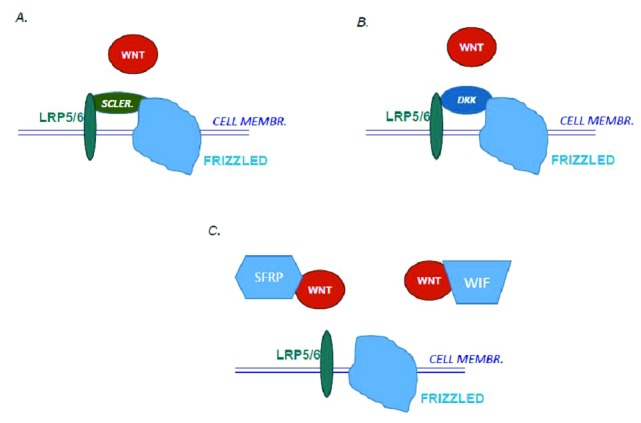
Different inhibitors can interact with WNT signaling. A. Sclerostin (Scler.) acts by binding to the extracellular part of the co-receptor LRP and thereby inhibits the binding of WNTs. Loss-of-function mutations in the SOST gene encoding sclerostin enhances binding of WNT and thereby increases WNT signalling and bone mass in patients with van Buchem´s disease and sclerosteosis. B. Dickkopf 1-4 (DKK) also binds to the extracellular part of the co-receptor LRP and inhibits binding of WNTs. C. Secreted Frizzled-related proteins (SFRP1-5) and WNT inhibitory protein (WIF) act as decoy receptors to bind soluble WNTs. Mutations in the SFRP4 gene are the cause of low bone mass in patients with Pyle´s disease.
