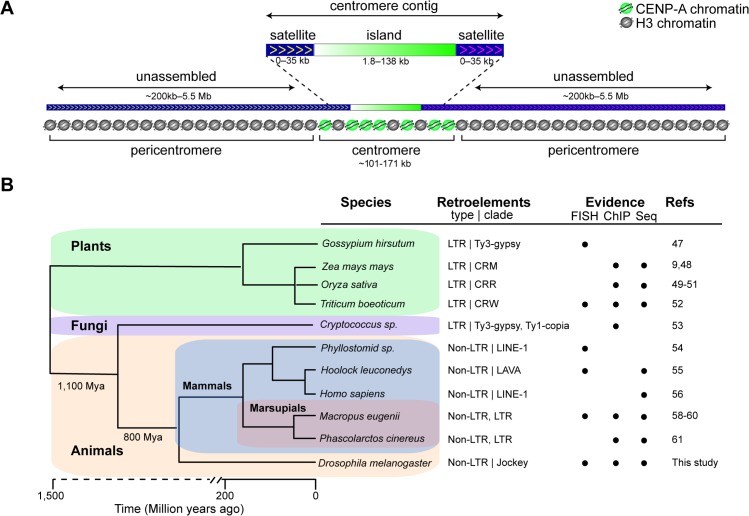
Fig 7. Drosophila centromere organization and widespread presence of retroelements at centromeres.
(A) Schematic showing the organization of D. melanogaster centromeres. For at least CenX, Cen4, and Cen3, the bulk of CENP-A chromatin is associated with the centromere islands, whereas the remaining CENP-A is on the flanking satellites. The sequences flanking the Y centromere are not in our assembly, so whether CENP-A is also on satellites is unknown. Although the complexity of island DNA allowed us to identify centromere contigs by long-read sequencing, the flanking satellites remain largely missing from our genome assembly because of their highly repetitive nature. The approximate satellite size estimates are based on Jagannathan and colleagues’ work [25]. (B) Phylogenetic tree showing that centromere-associated retroelements are common across highly diverged lineages: Gossypium hirsutum (cotton) [47], Zea mays mays (maize) [9, 48], Oryza sativa (rice) [49–51], Triticum boeoticum (wild wheat) [52], Cryptococcus [53], Phyllostomid (bat) [54], Hoolock leuconedys (gibbon) [55], Homo sapiens (human) [56] (and a human neocentromere [57]), Macropus eugenii (tammar wallaby) [58–60], Phascolarctos cinereus (koala) [61], and D. melanogaster (this study for endogenous centromeres; also in an X-derived minichromosome [14, 15]). The phylogeny was constructed using TimeTree [62]. Indicated are the retroelement type and the clade that the element belongs to with element types as follows: LTR and non-LTR. The circles indicate the experimental evidence for centromere association of retroelements: FISH, CENP-A ChIP-seq (ChIP), and genome or BAC sequencing (Seq). BAC, bacterial artificial chromosome; CENP-A, centromere protein A; CenX, X centromere; ChIP-seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing; CRM, centromeric retrotransposons of maize; CRR, centromeric retrotransposons of rice; CRW, centromeric retrotransposons of wheat; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; LAVA, LINE-Alu-VNTR-Alu-like; LINE, long interspersed nuclear element; LTR, long terminal repeat; Mya, million years ago.