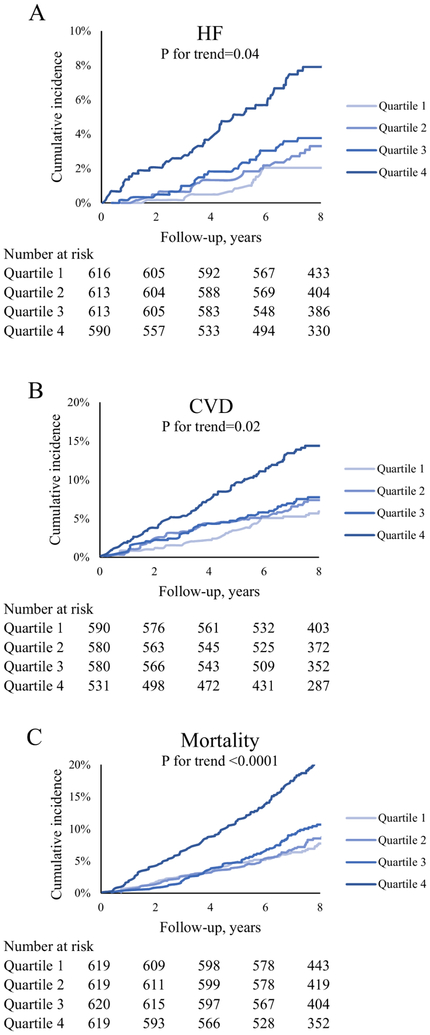
Figure 2. Cumulative incidence of HF, CVD, and mortality by classes of longitudinal change in galectin-3.
Persistently high levels of Gal-3 were associated with significantly higher risk of incident HF (A), incident CVD (B), and all-cause mortality (C). High-high, low-high, high-low, and low-low represent classes of change in Gal-3 between the earlier exam and the later exam using the clinical cut-off of 17.8 ng/ml. CVD = cardiovascular disease, HF = heart failure.