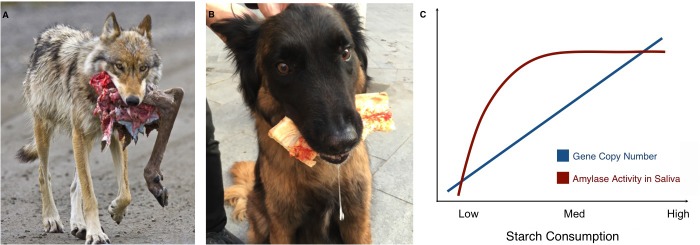
Figure 1. Links between proximity to humans, amylase gene copy number and amylase activity.
Animals that live alongside humans have diets that are different to those of their wild relatives, and these differences have led to dietary adaptations. While wolves (A) are highly carnivorous, dogs (B) have adapted to eating starchy human food scraps. (C) Pajic et al. found that species that consume medium or high amounts of starch have higher amylase activity in their saliva (maroon line) and more amylase gene copies (blue line) than species that consume little or no starch.
Image credit: A. NPS Photo/Ken Conger (CC BY 2.0); B. Mareike Janiak (CC BY 4.0)