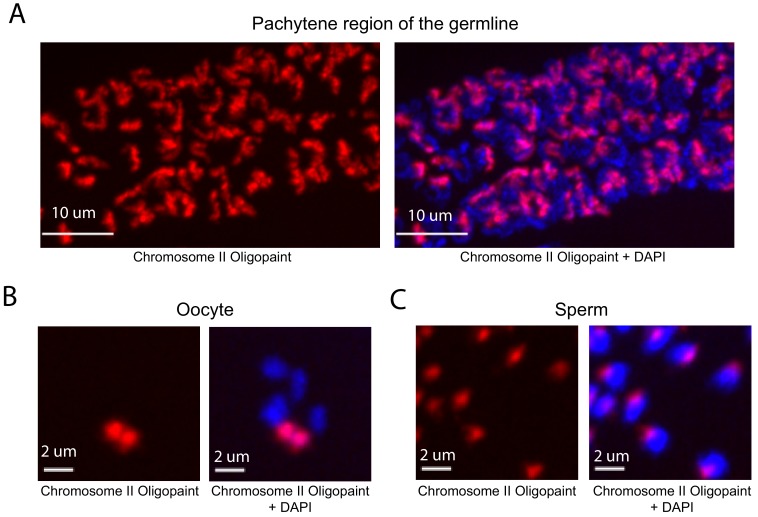
Figure 2. Whole chromosome Oligopaint in C. elegans is specific.
(A–C) Adult C. elegans were fixed as described in Materials and methods. Fixed animals were subjected to three step hybridization to detect Chromosome 2 (red). Animals were co-stained with DAPI (blue). (A) 3D maximum projection of the pachytene region of an adult C. elegans germline is shown. (B) 3D maximum projection of an oocyte. A single bivalent is stained with chromosome II Oligopaints. (C) 3D maximum projection of sperm. Scale bars for images are indicated. All images are representative of at least three independent animals.