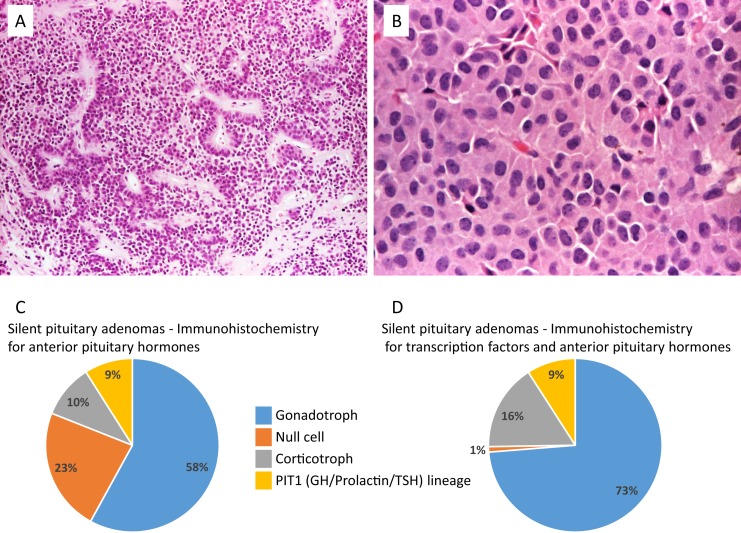
Figure 4.
True null cell adenomas are composed of uniform, mildly atypical cells with chromophobic cytoplasm. (A) An example showing sinusoidal, papillary, and pseudopapillary architecture similar to the more common gonadotroph adenomas (hematoxylin and eosin stain, ×10). (B) A case of oncocytoma consisting of large cells with acidophilic, granular cytoplasm (hematoxylin and eosin stain, ×20). (C and D) Prevalence of the different SPAs subtypes according to IHC for anterior pituitary hormones: silent gonadotroph adenomas were the most frequent, followed by null cell (according to the World Health Organization 2004 classification), corticotroph, and GH/prolactin/TSH lineage adenomas. The new classification using IHC for anterior pituitary hormones and transcription factor profiling substantially reduced the number of null cell adenomas. Derived from data from Nishioka H, Inoshita N, Mete O, et al. The complementary role of transcription factors in the accurate diagnosis of clinically nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas. Endocr Pathol 2015; 26:349-355.