Figure 1.
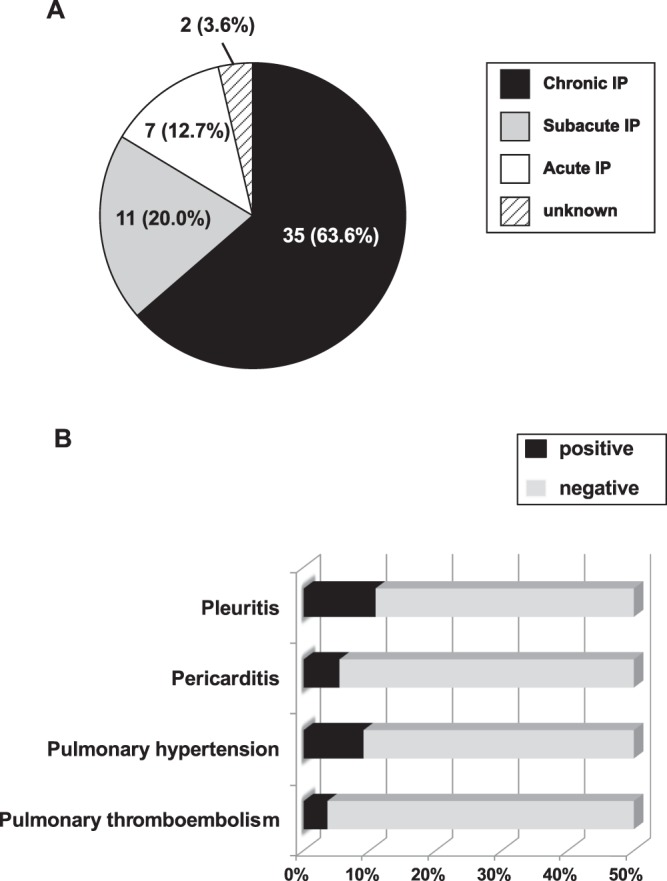
Forms of systemic lupus erythematosus-related interstitial pneumonia (SLE-IP) at onset and frequency of other SLE-related thoracic diseases in 55 patients with SLE-IP. (A) Chronic IP accounted for 35 patients (63.6%) followed by subacute IP (11 patients, 20%) and acute IP (seven patients, 12.7%). (B) The most frequent thoracic disease other than IP was pleuritis (six patients, 10.9%) followed by pulmonary hypertension (five patients, 9.1%), pericarditis (three patients, 5.5%), and pulmonary thromboembolism (two patients, 3.6%). Serositis, including pleuritis and pericarditis, was present in 16.4% of patients with SLE-IP.
