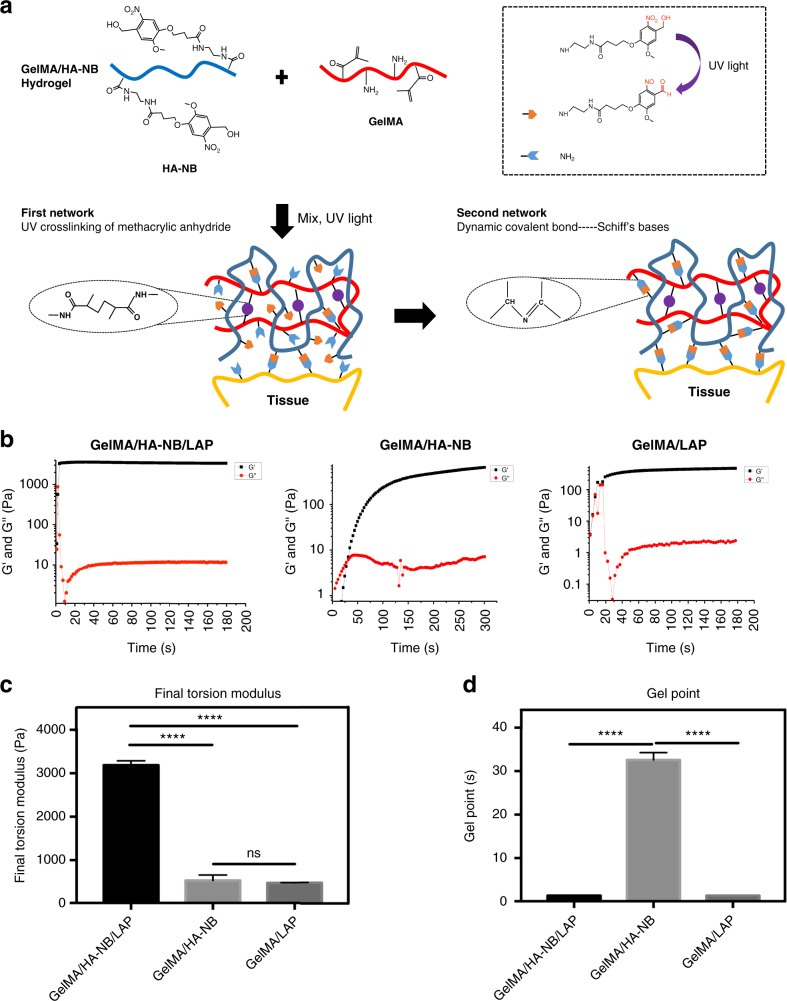
Fig. 1.
Chemical structure and mechanical properties of the hydrogels. a Constituent chemical structures and a schematic diagram illustrating the formation of the photo-triggered imine-crosslinked matrix hydrogel. b To monitor the gelling process, a dynamic time-sweep rheological analysis was carried out with an in situ photo-rheometer (HAAKE Mars III, light, Omnicure S2000 365 nm: 30 mW cm−2) showing the formation kinetics for GelMA/HA-NB/LAP, GelMA/HA-NB, and GelMA/LAP hydrogels. c The final torsion modulus G’ of different hydrogels. d The gel point of different hydrogels. All the gelling measurements were conducted using OmniCure S2000 (365 nm, 30 mW/cm2). Exposure time: 180 s for GelMA/HA-NB/LAP and GelMA hydrogels, and 300s for GelMA/HA-NB hydrogel (error bars, mean ± SD. ****p < 0.0001; NS: no significance, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Tukey’s post hoc test) (n = 3 per group). Source data are available in the Source Data file