Fig. 1.
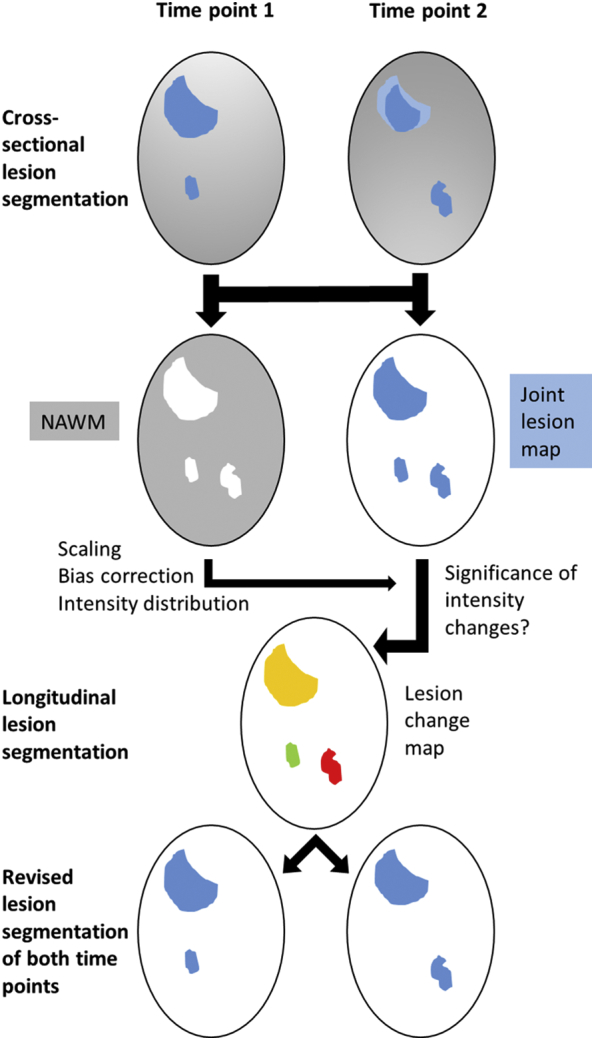
Overview on image processing for the segmentation of WML changes.
After coregistration of individual T1-weighted and FLAIR images and cross-sectional lesion segmentation, a joint lesion map is rendered. Normal appearing white matter (NAWM) is derived from the remainder (WM segmentation without WM lesions); after correction for the bias field, intensity scaling according to grey matter, the distribution of FLAIR intensity differences is estimated from NAWM differences to enable statistical testing for intensity changes within the joint lesion map. Significant changes are classified as increase (new lesion in red) or decrease (disappeared lesion in green). Non-significant changes but different cross-sectional lesion segmentation results are interpreted as lesion at both time points (yellow). For example, the large lesion fades out at its outer sections over time (light blue area at time point 2); since the intensity difference is not significant, no lesion change is indicated. For details, see text. NAWM, normal-appearing white matter.
