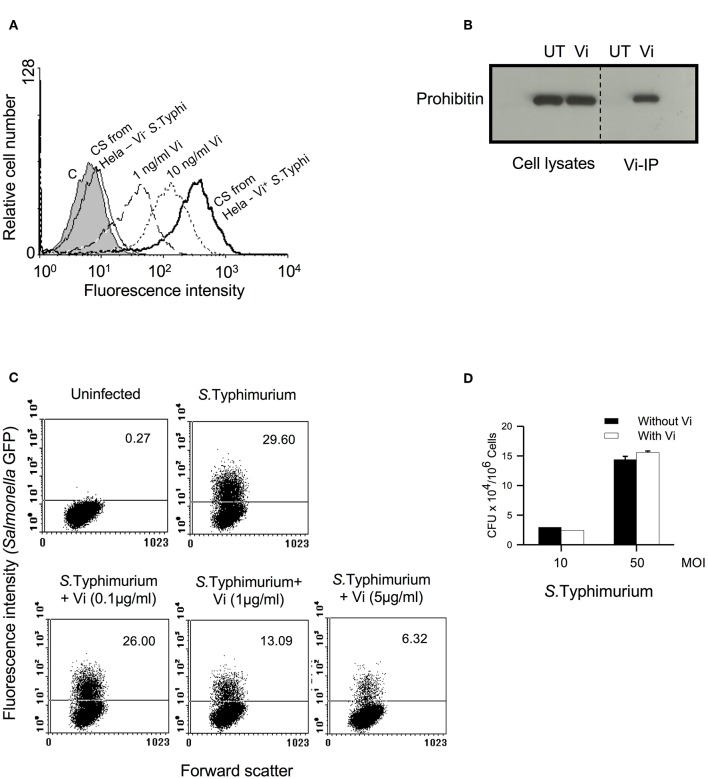
Figure 1.
Vi interacts with membrane prohibitin and inhibits invasion of epithelial cells with Salmonella. (A) Hela cells were incubated for 1 h at 4°C with different concentrations of Vi or cell-free culture supernatants (C.S) obtained from co-cultures of Hela cells with Vi+ or Vi− S. Typhi (100 MOI). Cells were washed and incubated with anti-Vi MoAb followed by FITC-labeled anti-mouse Ig Ab. Shaded histogram represents control cells, which were incubated only with anti-Vi MoAb and FITC-anti-mouse Ig Ab. Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. CS from Hela-S. Typhi-culture supernatant from Hela-S. Typhi co-culture. (B) Cells were incubated with Vi at 4°C for 1 h and lysed with Triton X-100 (1%). Vi-interacting proteins were immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with anti-Vi MoAb loaded on Protein G-Sepharose. Proteins were electrophoresed in a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel, transferred to nitrocellulose membrane and probed with anti-prohibitin antibody. The blot was developed using ECL. UT, untreated cells; Vi, Vi-treated cells. (C) Cells were infected with GFP+ S. Typhimurium (50 MOI) in the absence or presence of indicated concentrations of Vi, washed to remove unbound bacteria and incubated for another 30 min in presence of gentamycin (100 μg/ml). Cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde and analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) Cells were incubated with S. Typhimurium in the absence or presence of Vi at 4°C, washed to remove unbound bacteria and lysed with PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100. CFUs were determined by plating cell lysates on SS-Agar. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments.