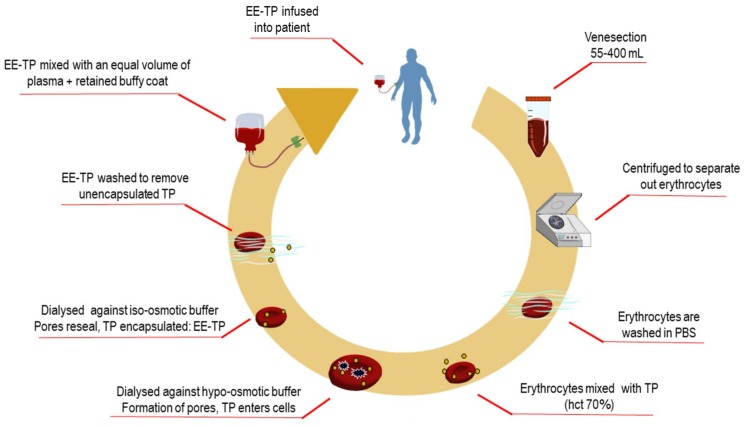
Figure 2.
Manufacture of erythrocyte-encapsulated thymidine phosphorylase (EE-TP). Following venesection, blood was transferred to a Class A isolator for the manufacture of EE-TP under a Specials according to the Rules and Guidance for Pharmaceutical Manufacturers 2007 (MHRA). Blood was centrifuged to separate components and then the erythrocytes washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Erythrocytes were then mixed with an appropriate activity of thymidine phosphorylase (TP) to a haematocrit of 70% and then dialysed against hypo-osmotic buffer for 90 min to create pores in the cell membrane. The lysed erythrocytes were then resealed by dialysis against iso-osmotic buffer for 60 min to encapsulate TP that had entered the cells. The resulting EE-TP was then washed to remove encapsulated TP, mixed with the retained buffy coat and an equal volume of autologous plasma, and then infused into the patient.