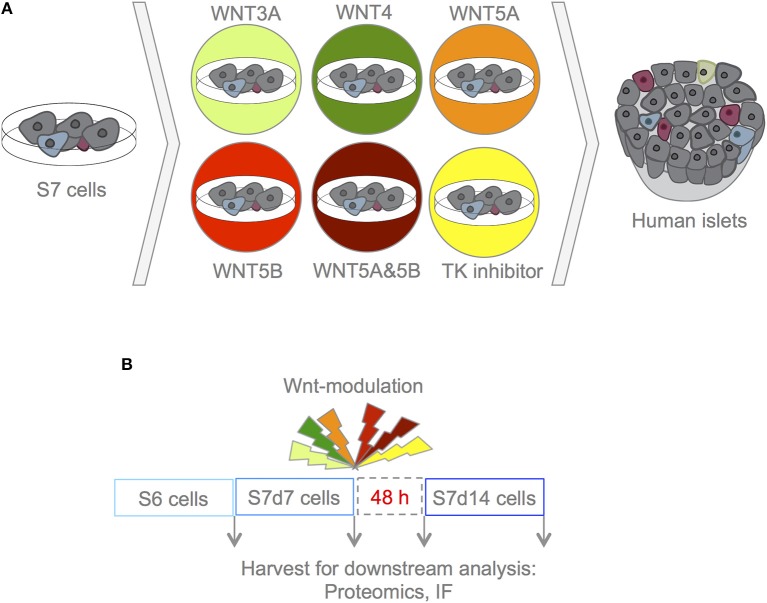
Figure 1.
Experimental design. (A) With this experimental set-up we aimed to assess whether Wnt-modulation could drive maturation of S7 cells toward a phenotype that closer resembles that of β-cells as found in adult human islets. To assess the effects of Wnt-modulation of S7 cells, the Wnt-modulated cells were compared to un-stimulated S7 cells as well as to adult human islets. (B) S7d7 cell cultures were treated for 4 h with either WNT3A (light green), WNT4 (green), WNT5A (orange), WNT5B (red), a combination of WNT5A&5B (dark red) for stimulation of the canonical or non-canonical Wnt pathways, or TKi (yellow) to block endogenous Wnt signaling in S7d7 cell cultures. The Wnt-modulated S7 cells were maintained in differentiation culture for 48 h prior to harvest for downstream analysis [including proteomics analysis and immunofluorescence (IF)].