Fig. 2.
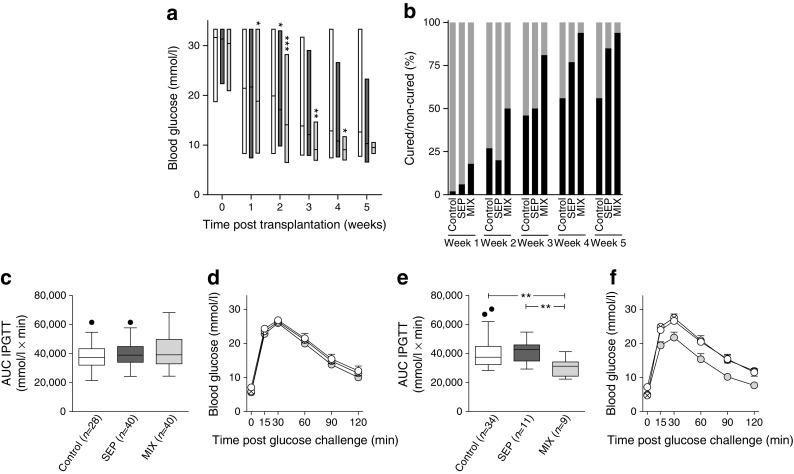
In vivo function of a marginal islet mass co-transplanted with human MAPCs. (a) Blood glucose measurements of alloxan-induced diabetic C57BL/6 mice transplanted with 150 islets alone (control [n = 47]; white bars) or with 150 islets co-transplanted as separate (n = 52; dark-grey bars) or composite pellets (n = 40; light-grey bars) with 2.5 × 105 human MAPCs. Floating bars extend from the minimum to the maximum, the line indicates the mean.*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 vs islets alone (control). (b) Percentage of cured (black bars) and non-cured (grey bars) mice after islet transplantation. (c–f) AUCs and blood glucose measurements after IPGTTs in mice transplanted with a marginal islet mass alone (control, white circles) or combined with human MAPCs as a separate (crossed circles) or composite pellet (grey circles) 2 (c, d) and 5 (e, f) weeks after transplantation. **p < 0.01 for indicated comparisons. The box extends from the 25th to 75th percentiles, the line indicates the median, and the Tukey method was used to plot the whiskers and the outliers (solid black dots); (d, f) mean ± SEM
