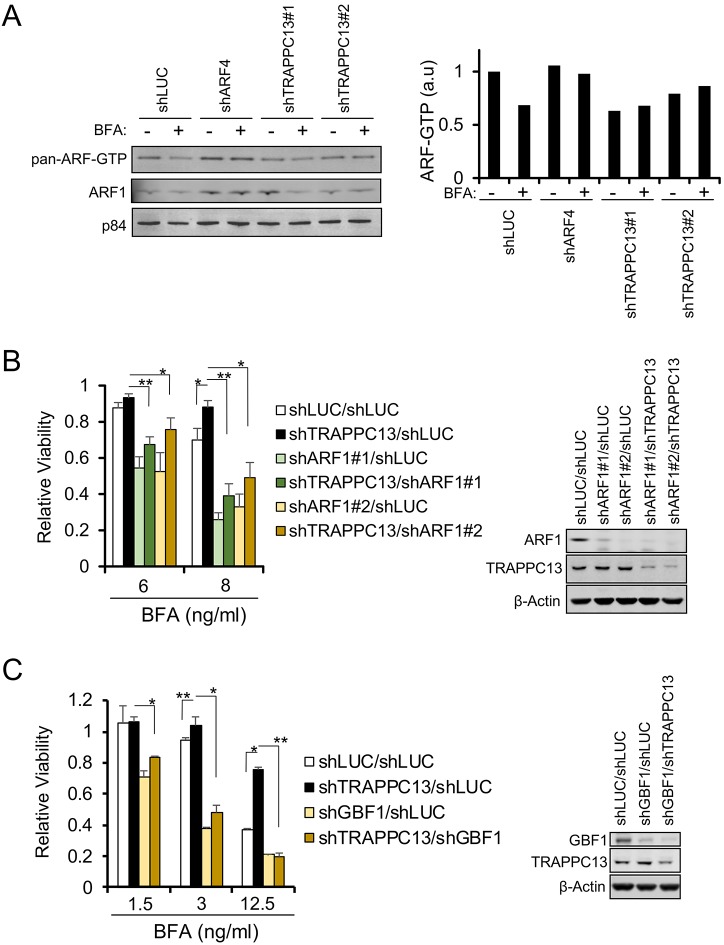
Fig. 3.
ARF1 and GBF1 contribute to BFA resistance in TRAPPC13 knockdown cells. (A) Stable shLUC-transduced control, shARF4 (positive control) or TRAPPC13 knockdown A549 cells were analyzed for total ARF-GTP levels in the absence or presence of 20 ng/ml BFA (24 h treatment) using a GST-VHS-GAT pulldown assay. In this assay, increased ARF binding to VHS-GAT, a truncated GGA3 form and ARF-substrate that only interacts with GTP-bound ARFs, serves as an indicator of ARF activity. Pan-ARF indicates the use of an antibody (1D9), which recognizes all five mammalian ARF isoforms, whereas (1A9/5) specifically detects ARF1 (see also Materials and Methods). A representative quantification from two independent experiments is shown; a.u., arbitrary units. (B,C) Reducing (B) ARF1 or (C) GBF1 function in A549 TRAPPC13 knockdown cells using several independent shRNAs reverses BFA resistance observed in TRAPPC13 single knockdown cells. Cells were treated (B) for 3 days with 6 or 8 ng/ml BFA or (C) for 2 days with 1.5, 3, 12.5 ng/ml BFA; at least five wells per condition were measured. The survival ratio was determined by performing a CTB assay. Data represent at least three independent experiments. **P<0.01, *P<0.05. Western blots of co-depleted cells are shown to confirm knockdown of the indicated proteins.