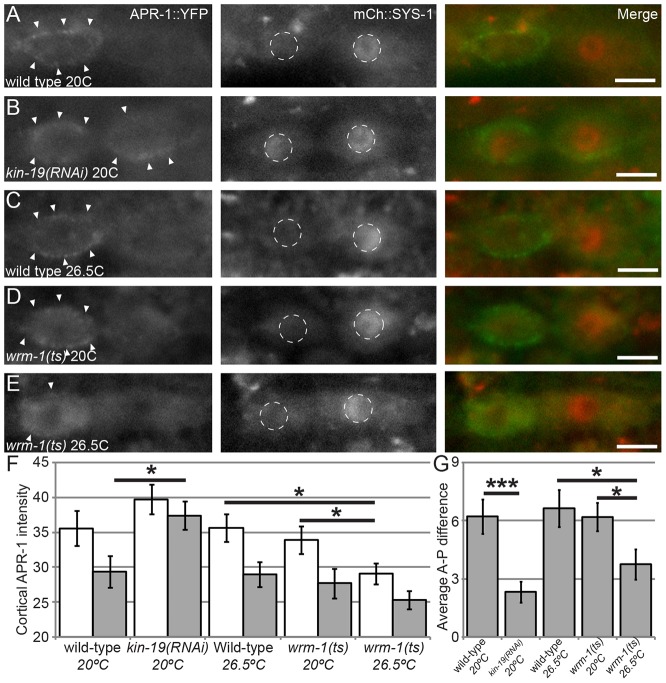
Fig. 6.
KIN-19 controls APR-1 and SYS-1 localization, whereas WRM-1 controls only APR-1. All images show osIs13(APR-1::YFP); uIwIs4(mCherry::SYS-1). (A) Wild-type control. Cortical APR-1::YFP (left, arrowheads; green in merge) and nuclear SYS-1::mCherry (center, white dashed circles; red in merge) display proper asymmetric localizations (merge on right). (B) kin-19(RNAi). (C) Wild-type seam cell held at 26.5°C for 3 hours prior to division. (D) wrm-1(ne1982) at the permissive temperature of 20°C. (E) wrm-1(ne1982) at the restrictive temperature of 26.5°C for 3 hours prior to division. Reduced cortical levels of APR-1::YFP were observed but no changes in SYS-1 nuclear asymmetry were observed. Arrowheads, cortical APR-1 localization; white dashed circles, nuclei. Scale bars: 5 µm. (F) Quantification of cortical APR-1::YFP fluorescence above backgrounds. White bars, anterior daughters; gray bars, posterior daughters. (G) Average anterior-posterior (A-P) difference in cortical APR-1::YFP fluorescence. ts, temperature sensitive. The n values are as follows: EV at 20°C, n = 23; kin-19(RNAi) at 20°C, n = 24; wild-type at 26.5°C, n = 25; wrm-1(ne1982) at 20°C, n = 26; wrm-1(ne1982) at 26.5°C, n = 28. Data show the mean±s.e.m.; *P<0.05; ***P<0.001.