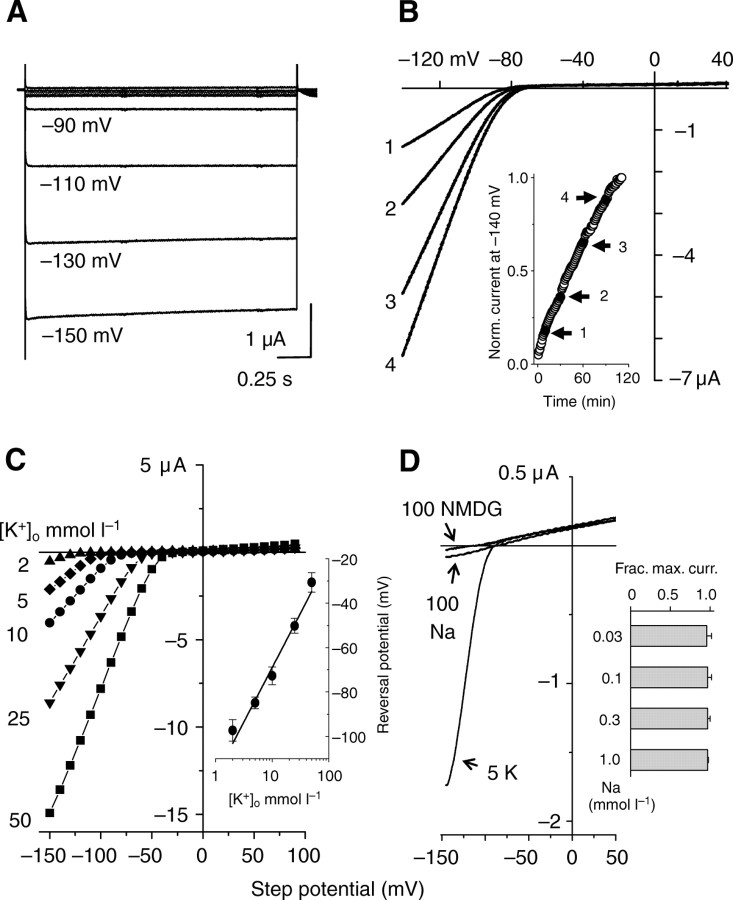
Fig. 3.
Heterologous expression of sponge inward-rectifier potassium (Kir) channels. Strongly rectifying currents in 5 mmol l–1 external K+ (KMES) recorded from (A) AmqKirA using 2 s voltage steps from– 150 to +100 mV in +20 mV increments from a holding potential –50 mV and (B) AmqKirB using a voltage ramp from a holding potential of –50 mV. Current–voltage plots for AmqKirB taken at 10 (#1), 30 (#2), 60 (#3) and 90 (#4) mins. The inset shows, in the same cell, the time-dependent change in the normalized current at –140 mV (until the recording ended). (C) Effect of increasing external K+ on AmqKirA currents. Solutions of 2, 5, 10, 25 and 50 mmol l–1 KMES were used. The inset is a semi-log plot of the reversal potential versus external K+ concentration for AmqKirA (N=6–28 per concentration, means± s.e.m.). The fitted line has a slope of 49 mV. (D) Representative AmqKirA current–voltage relationships recorded in 5 mmol l–1 K+, 100 mmol l–1 NMDG, and 100 mmol l–1 Na (all used as MES salts) showing no Na or NMDG permeability. The inset shows results of the test of Na (0.03–1 mmol l–1 NaCl) block of 5 mmol l–1 KMES currents (N=5, means ± s.e.m.).