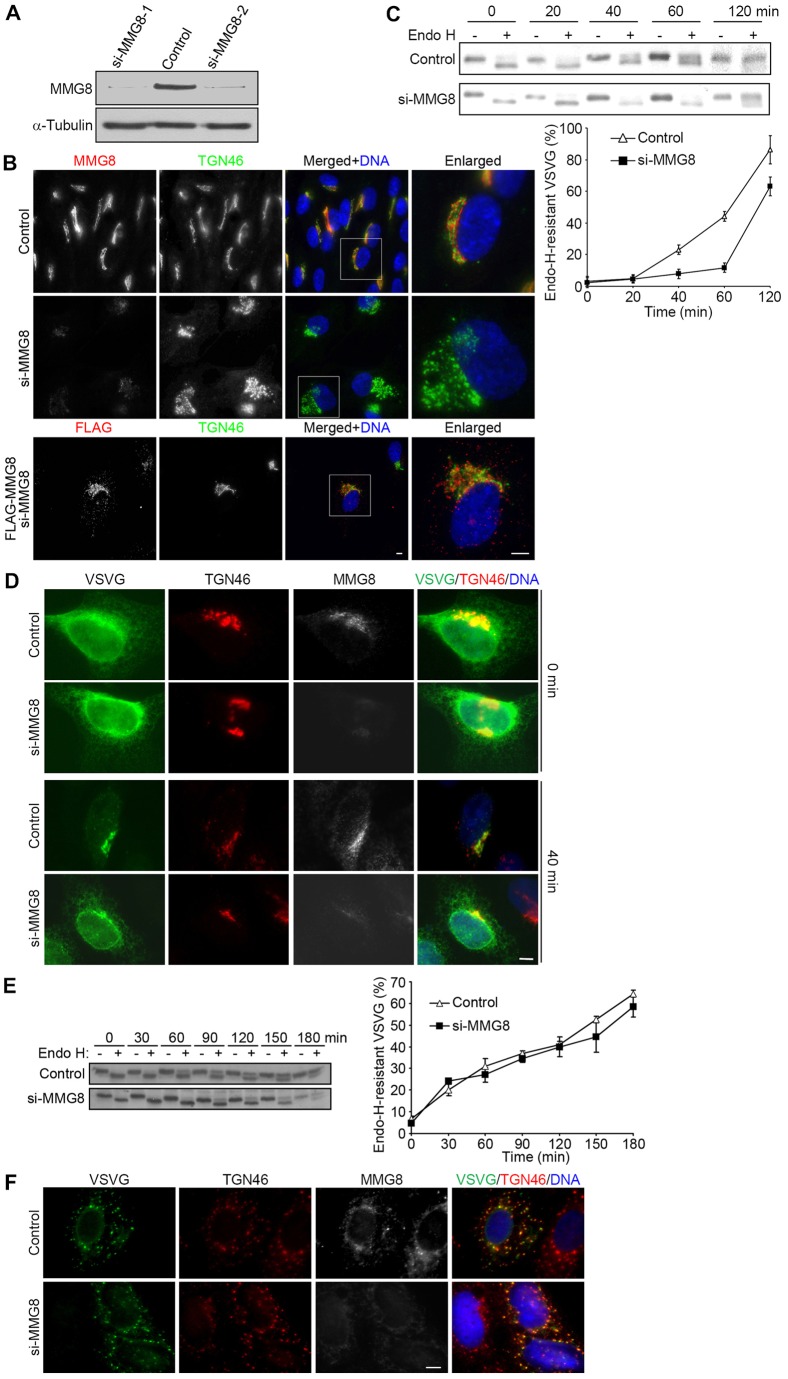
Fig. 2.
MMG8 is required for Golgi structural organization and efficient ER-to-Golgi transport. (A) Immunoblotting of HeLa cells transfected with control or mmg8-targeting siRNAs. The transfection of MMG8 siRNAs (si-MMG8-1 and si-MMG8-2) suppressed the expression of the protein by ∼85%. (B) RPE1 cells transfected with control or mmg8-targeting siRNA were analyzed using immunofluorescence microscopy. The knockdown of MMG8 was rescued by the transfection of an siRNA-resistant construct (FLAG–MMG8). The boxed regions are enlarged on the right. The figure shows micrographs that are representative of ∼1000 cells (n = 3). (C) HeLa cells were transfected with VSVG–YFP. The cells were extracted at various times during incubation at 32°C and were assayed for endo-H resistance. Following the assay, the samples were immunoblotted to check for VSVG. The amounts of the endo-H-resistant form of VSVG relative to the total amounts of VSVG were determined, and quantitative data from three independent experiments are presented here as the mean±s.d. (D) Cells were fixed at 0 or 40 min of 32°C incubation and then immunostained. At least 90% of the 200 cells analyzed for each condition exhibited the phenotypes shown. (E,F) Cells expressing VSVG–YFP were treated with 10 µg/ml nocodazole at 40°C for 6 h and then shifted to 32°C and incubated further. The figure shows the results of the endo-H-resistance assay (E) of cells collected at various times (from three independent experiments; data show the mean±s.d.) and representative images of cells (>90% of 100 cells) that were fixed after incubation for 15 min at 32°C (F). Scale bars: 5 µm.