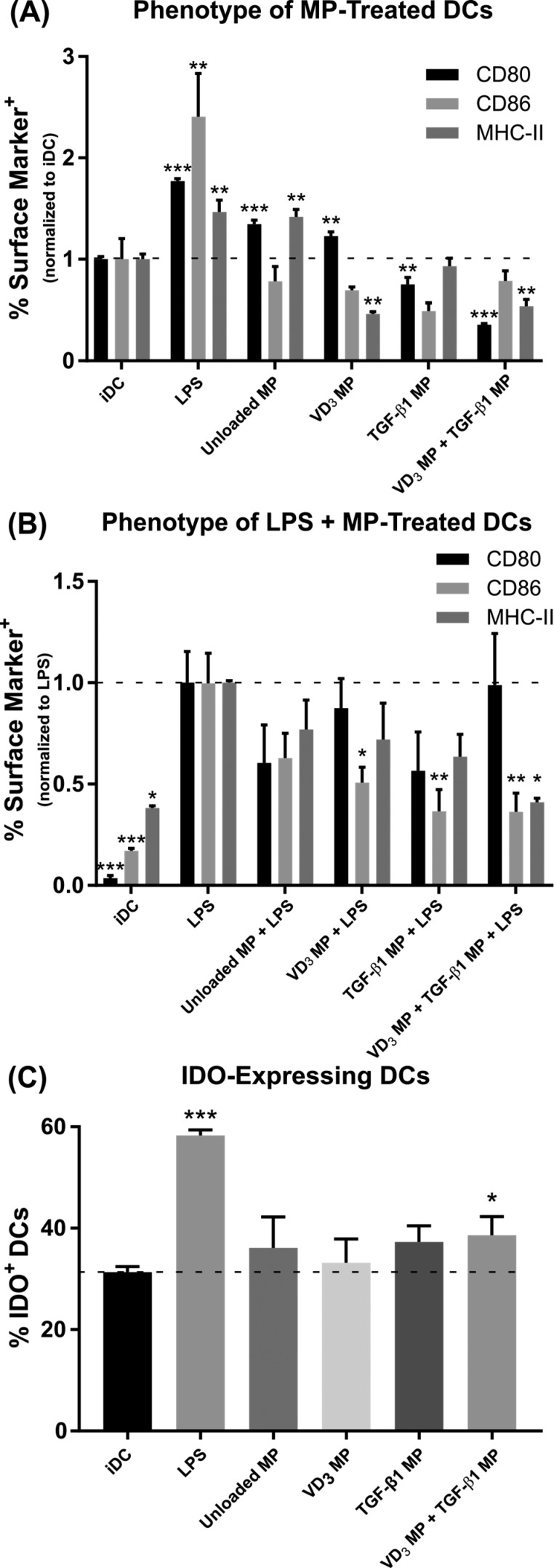
Figure 3.
Co-incubation of vitamin D3(VD3) MPs and TGF-β1 MPs induce DCs with suppressive phenotypes in vitro. Dendritic cells were incubated with 10 mg of nonphagocytosable TGF-β1 MPs, and phagocytosable VD3 MPs were added at a 10:1 MP to DC ratio. Microparticles were incubated with bone marrow-derived DCs for 48 h and subsequently washed with PBS to remove MPs. Untreated, immature DCs (iDC), DCs stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL), and DCs incubated with unloaded MPs were included as controls. (A) Maturation markers CD80, CD86, and MHC-II were characterized by flow cytometry on MP-treated DCs and controls (n = 3). Surface expression is normalized to iDCs. (B) Maturation resistance in response to LPS was quantified (n = 3). Dendritic cells were stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 24 h following MP treatment. Flow cytometric analysis quantified expression of CD80, CD86, and MHC-II. Surface expression is normalized to LPS stimulated DCs. (C) Dendritic cell expression of the immunosuppressive enzyme IDO was quantified in response to MP treatment (n = 3). P-values (∗ = ≤0.05, ∗∗ = ≤0.01, ∗∗∗ = ≤0.001) were obtained by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test against the iDC control (A, C) or the LPS-stimulated control (B). Data are represented by the mean ± SEM.