Fig. 1.
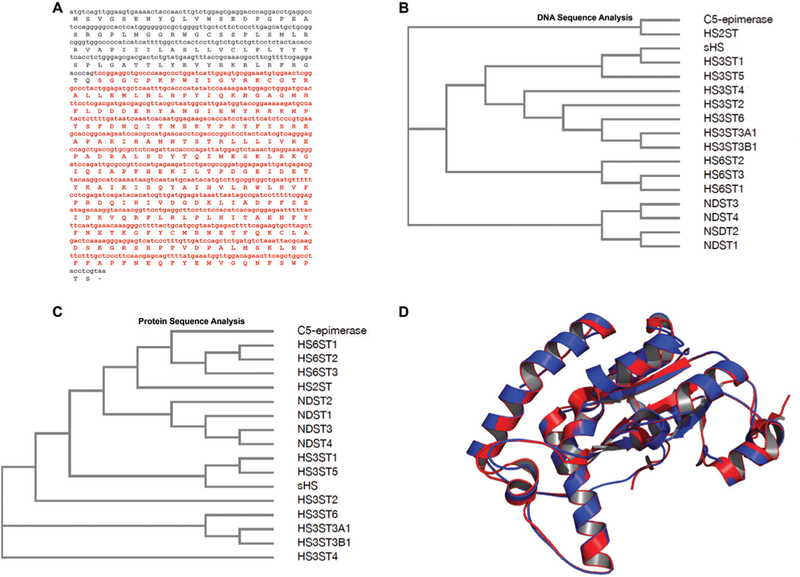
Composite DNA, predicted amino acid sequences and structural model for the shrimp Litopenaeus vannameisulfotransferase. (A) The nucleotide fragment as well as the amino acid sequence in red are related to enzymatic domains responsible for the carbohydrate and PAPS binding. This cDNA sequence (red) was cloned in pRSET A. Amino acid sequence was predicted by using Expasy (http://web.expasy.org/translate/). (B) Cladogram analysis of DNA sequences demonstrates that the isoforms 1 and 5 of 3-O-sulfotransferase (HS3ST) from Homo sapiensdisplay higher identity to sHS. (C) Cladogram analysis of amino acid sequences confirms that the highest similarity is among isoforms 1 and 5 of HS3ST to sHS. (D) Comparison between tertiary structures of sHS from shrimp L. vannamei(red) and HS3ST5 from Homo sapiens(blue). The 3D structure of sHS was modeled based on the human 3-O-sulfotransferase isoform 5 crystal structure (PDB #3BD9) using SWISS-MODEL.37 Structural alignment was performed on The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8 Schrödinger, LLC. Abbreviations: NDST: N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase; HS2ST: 2-O-sulfotransferase; HS3ST: 3-O-sulfotransferase; the isoforms of each enzyme correspond to numbers from 1 to 6.
