Fig. 2.
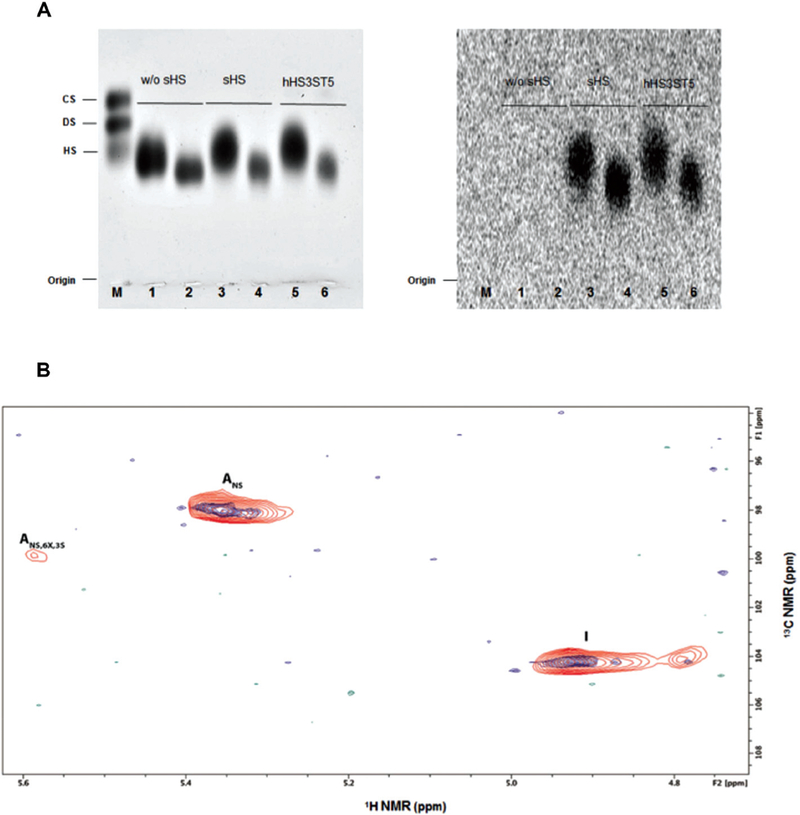
sHS substrate selectivity. (A) Activity assay on modified heparins. 1, 3 and 5: Substrate used was O,N-desulfated-N-resulfated heparin (25 of uronic acid); 2, 4 and 6: using as the substrate O,N-desulfated-N-reacetylated heparin (25 ĝ of uronic acid). In 1 and 2, the reaction mixture did not have the recombinant enzyme in their preparations. Left: PDA gel stained with toluidine blue. Right: PDA gel exposed for three days to radiation sensitive films. Both sHS enzyme as well as recombinant human HS3ST5 were able to transfer [35]S-sulfate to chemically modified heparins. M: Mixture of standard glycosaminoglycans containing chondroitin sulfate (CS), dermatan sulfate (DS) and heparan sulfate (HS) (5 ĝ each). (B) Description of compound HepNSulfo[35]S-sulfate, previously modified by sHS, by two-dimensional heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) NMR. The HepNSulfo control (blue) and the HepNSulfo[35]S-sulfate (red) spectra displayed similar components, whereas the HepNSulfo[35]S-sulfate showed the presence of 3-O-sulfated glucosamine (ANS,6X,3S), indicating that sHS is indeed a 3-O-sulfotransferase. Abbreviations: I: iduronic acid, Ans: glucosamine N-sulfated and ANS,6X,3S: glucosamine N,3-sulfated, where 6X could be 6OH or 6S.
