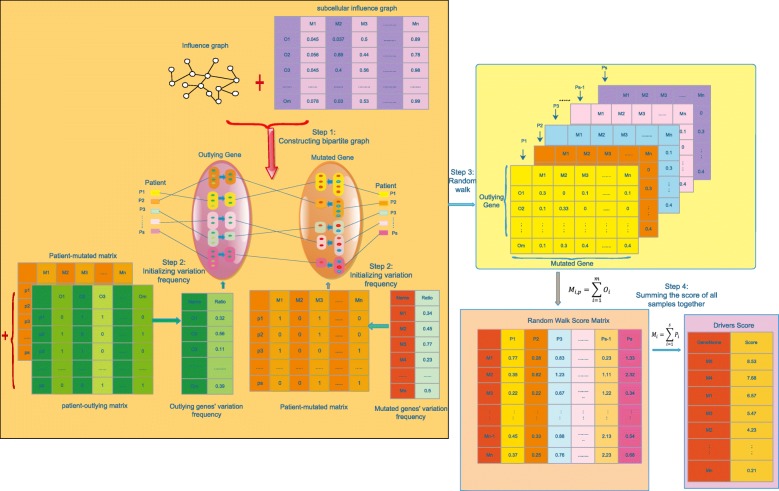
Fig. 1.
The workflow of Subdyquency. The left part with yellow background color represents the process to generate a walking score of each mutated gene for each patient. At first, we constructed the bi-partite graph between the outlying genes (dark green nodes) and mutated genes (red nodes) for each patient according to their relationship in influence graph (step 1). Each pair of interactions between mutated genes and outlying genes in bipartite graph was assigned a reliability weight according to the common subcellular compartments they belong to (top part). Then, we calculated the variation frequency for each filtered mutated genes and outlying genes as the initialized value (step 2). After random walk with three times, the walking score for each patient can be drawn (step 3). We integrated the walking score by summing up the outlying genes’ value of each mutated gene across all patients (pink background). We calculated the final score for each mutated gene by summing up its value across patients and ranked them in a descending order