Fig. 3.
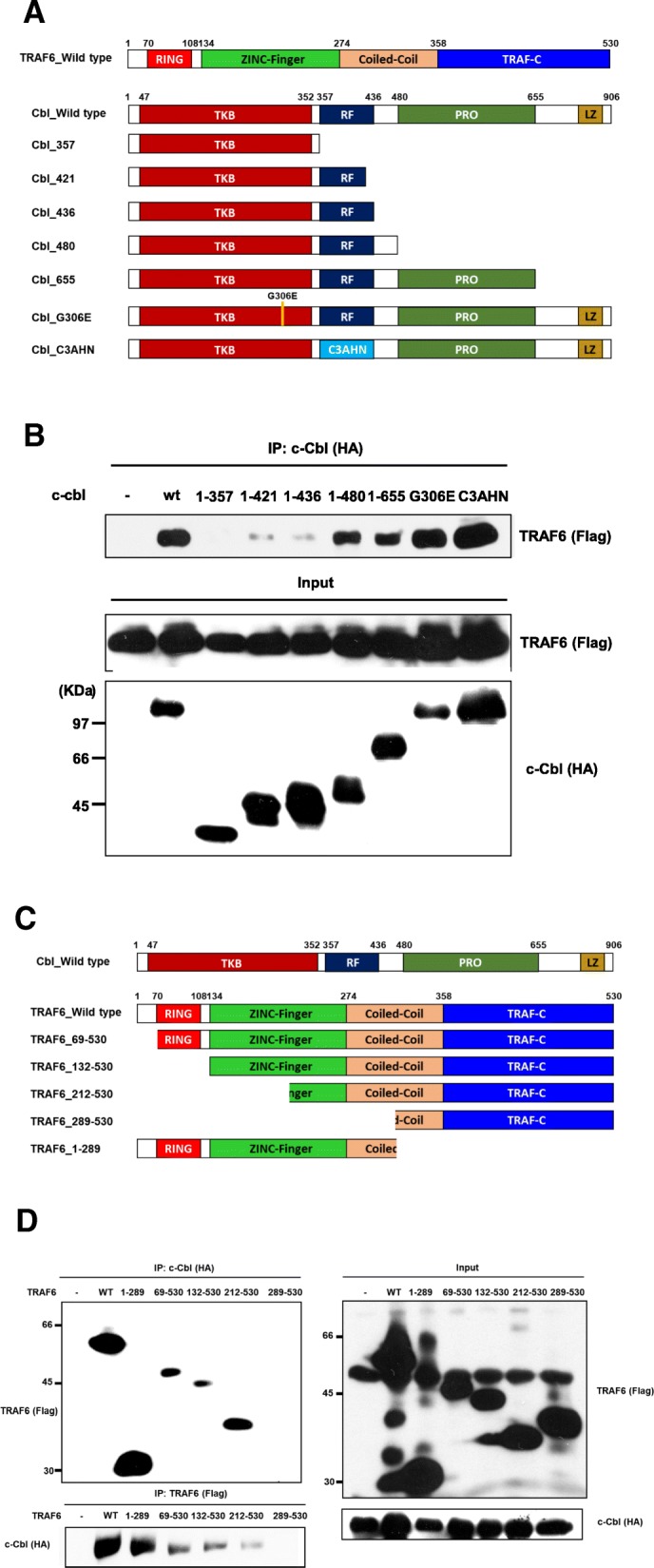
c-Cbl interacts with TRAF6 through the c-terminus of c-Cbl and N-terminus of TRAF6. a – Schematic illustration of wild-type TRAF6, wild-type c-Cbl and its mutants: TKB, tyrosine kinase-binding domain; RF, RING finger domain; PRO, proline-rich region; and LZ, leucine zipper. The number for each mutant indicates the Cbl residue that constitutes the c-terminus in the mutant protein. b – 293 T cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged TRAF6 (2 μg) together with expression plasmids encoding HA-tagged wild-type Cbl (WT), Cbl-G306E mutant (G306E), Cbl-C3AHN mutant, or various truncation mutants of Cbl, as indicated. After 36 h of transfection, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA Ab and then probed with anti-FLAG-TRAF6. Controls for the expression of FLAG-TRAF6 and HA-cbl are shown (middle and bottom panels). c – A schematic illustration of wild-type c-Cbl, wild-type TRAF6 and its mutants: RING, RING finger domain; and Zn FINGER, Zinc finger domain. d – 293 T cells were transfected with HA-tagged c-Cbl (2 μg) together with expression plasmids encoding FLAG-tagged wild-type TRAF6 (WT) or various truncation mutants of TRAF6, as indicated. After 36 h of transfection, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA or anti-FLAG Abs and then probed with anti-HA or anti-FLAG, respectively (left panels). Controls for the expression of FLAG-TRAF6 and HA-c-Cbl are shown (right panels)
