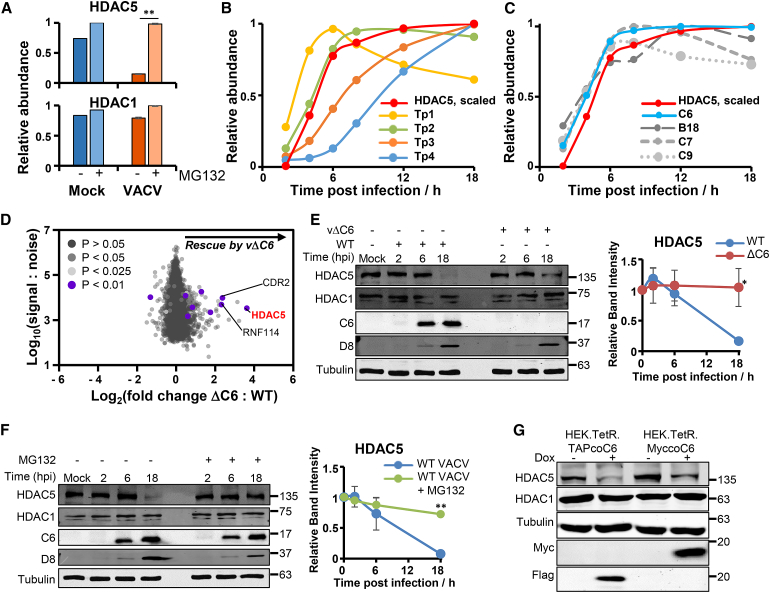
Figure 6.
VACV Protein C6 Downregulates HDAC5
(A) HDAC5, but not HDAC1, is proteasomally degraded during VACV infection. Bar charts and statistics were generated as described in Figure 5.
(B) Viral class centroid profiles compared to an inverted profile of HDAC5, which had additionally been scaled from 0 to 1.
(C) Profile of HDAC5 scaled as in (B), and Tp2-class VACV proteins with known roles in regulation of IFN or ISGs.
(D) C6 targets HDAC5. HFFF-TERTs were infected in biological triplicate with WT VACV or vΔC6 (lacking gene C6L) (Unterholzner et al., 2011) (MOI = 5 and 12 h). The scatterplot shows all proteins quantified. A Benjamini-Hochberg-corrected two-tailed t test was used to estimate p values.
(E) Representative immunoblot demonstrating that C6 specifically targets HDAC5. By comparison, HDAC1 was unmodified (MOI = 5). Quantitation of all three replicate immunoblots are shown (right panel). Data are represented as mean ± SEM, ∗p < 0.05 from a two-tailed t test.
(F) Representative immunoblot demonstrating rescue of HDAC5 expression by inhibition of the proteasome (MOI = 5). MG132 was added 2 h after VACV infection. Quantitation of all three replicate immunoblots is shown (right panel). Data are represented as mean ± SEM, ∗∗p < 0.00005 from a two-tailed t test.
(G) Immunoblot demonstrating that inducible expression of C6 is sufficient for HDAC5 degradation. HEK293T cells inducibly expressing C6 with an N-terminal Myc or C-terminal TAP tag were either treated or untreated with 100 ng/ml doxycycline overnight then lysates immunoblotted.