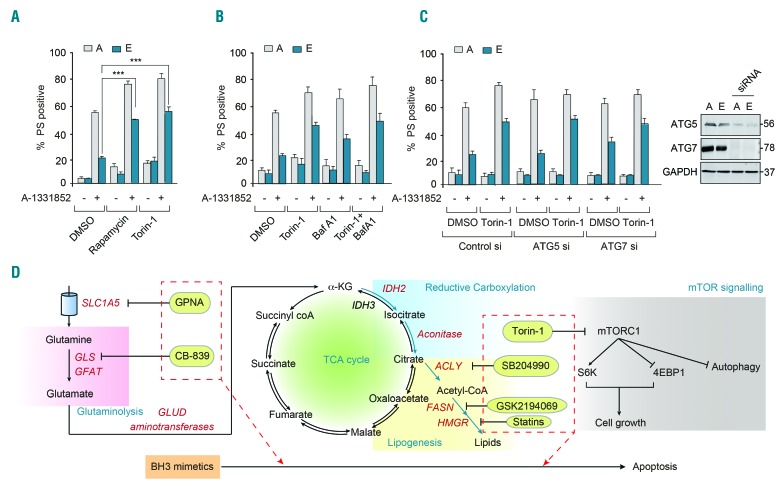
Figure 5.
Modulation of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling enhances sensitivity to BH3 mimetics independently of autophagy. (A) Apoptotic sensitivity of K562 resistant [E] cells exposed to A-1331852 (10 nM) for 4 h was restored following pharmacological inhibition of mTOR signaling using rapamycin (100 nM) or torin-1 (10 nM) for 16 h. (B) Inhibition of mTOR-regulated autophagy using 3-MA (10 mM) or bafilomycin A1 (100 nM) for 1 h, followed by torin-1 (10 nM) for a further 16 h, resulted in varying effects on A-1331852-mediated apoptosis. (C) Genetic knockdown of ATG5 and ATG7 for 72 h failed to revert torin-1 (10 nM)-mediated sensitization of apoptosis in K562 resistant [E] cells, following A-1331852 (10 nM) for 4 h. Western blots confirmed the knockdown efficiency of ATG5 and ATG7 short interfering (si) RNA. ***P⩽0.001. Error bars = mean ± standard error of mean (n=3). (D) Scheme representing glutamine uptake by SLC1A5 (inhibited by GPNA), glutaminolysis (inhibited by CB-839) to generate α-ketoglutarate, reductive carboxylation of α-ketoglutarate to generate citrate, which produces acetyl-CoA by a reaction catalyzed by ACLY (inhibited by SB204990), which eventually results in lipogenesis (inhibited by GSK2194069) and cholesterogenesis (inhibited by statins). Glutamine uptake, metabolism and its downstream signaling cascade can feed into mTOR signaling (inhibited by torin-1), all of which promote cell growth. In this study, we demonstrate that modulation of these distinct intermediary metabolic pathways could successfully sensitize cancer cells to BH3 mimetic-mediated apoptosis. PS: phosphatidylserine; DMSO: dimethylsulfoxide; TCA: tricarboxylic acid.