Figure 5.
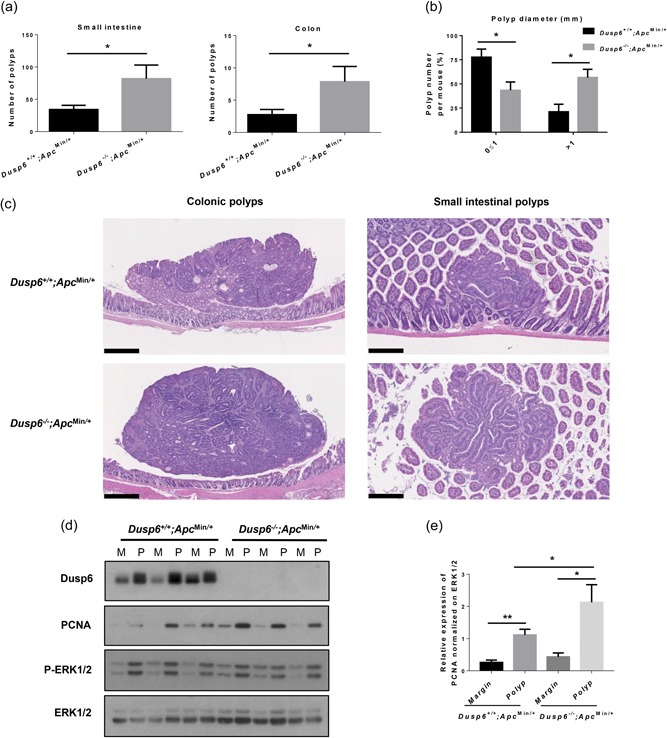
Dusp6 deletion increases intestinal tumorigenesis in Apc Min/+ mice. (a) Polyp numbers were counted in 13‐week‐old Dusp6 +/+ ; Apc Min/+ and Dusp6 ‐/‐; Apc Min/+ small intestine and colon (n ≥ 7). (b) Small intestinal polyp size (diameter) was compared between Dusp6 +/+ ; Apc Min/+ and Dusp6 ‐/‐;Apc Min/+ mice (n = 5). (c) Dusp6 +/+; Apc Min/+ and Dusp6 ‐/‐; Apc Min/+ polyp histology was visualized with hematoxylin and eosin staining in the small intestine (scale bars: 250 µm) and colon (scale bars: 500 µm; representative of n ≥ 4). (d) Dusp6, PCNA, and phosphorylated ERK1/2 levels were analyzed by western blot of polyp (P) and healthy marge (M) protein extracts (n = 3). ERK1/2 expression was used as loading control. Representative immunoblots are shown. (e) Densitometric analysis of PCNA expression relative to ERK1/2 (n = 7). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Student’s t test; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. DUSP6: dual‐specificity phosphatase 6; ERK: extracellular signal‐regulated kinase; PCNA: proliferating cell nuclear antigen
