Figure 6.
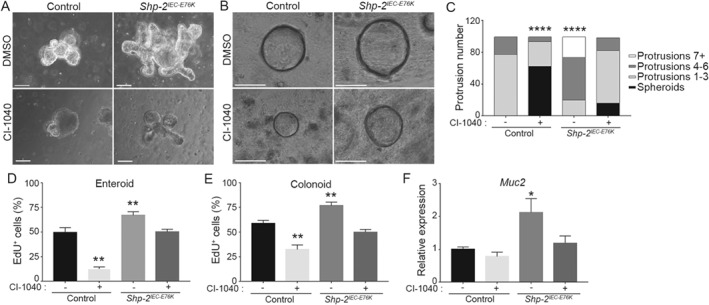
Shp‐2 drives crypt regeneration through ERK/MAPK pathway. Intestinal crypt enteroids and colonoids from Shp‐2 IEC‐E76K or control mice were cultured in Matrigel for 12 h before treatment with the MEK inhibitor CI‐1040 (8 μm) or DMSO. Images present (A) enteroids and (B) colonoids cultured for 4 days with or without MEK inhibitor. Scale bars = 50 μm. (C) At day 4, protrusion numbers from 100 control or Shp‐2 IEC‐E76K enteroids were counted for each condition. The graph presents the percentage of organoids with a certain number of protrusions. A representative experiment is shown. n = 5. EdU incorporation staining was used to measure proliferation in control and Shp‐2 IEC‐E76K enteroids (D) and colonoids (E), treated with or without CI‐1040 at 8 μm for 4 days. For enteroids, EdU‐positive cells per protrusion were counted. For colonoids, EdU‐positive cells were counted per whole organoid. Approximatively 100 organoids were analyzed per condition and the experiments were conducted with n = 5 mice. (F) Muc2 gene expression by RT‐qPCR in control and Shp‐2 IEC‐E76K enteroids with or without MEK inhibition. Expression was normalized to the reference transcripts Psmc4, Pum1 and Tbp. n = 5. Graphs present mean ± SEM. Student's t‐test *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ****p ≤ 0.0001.
