Figure 4.
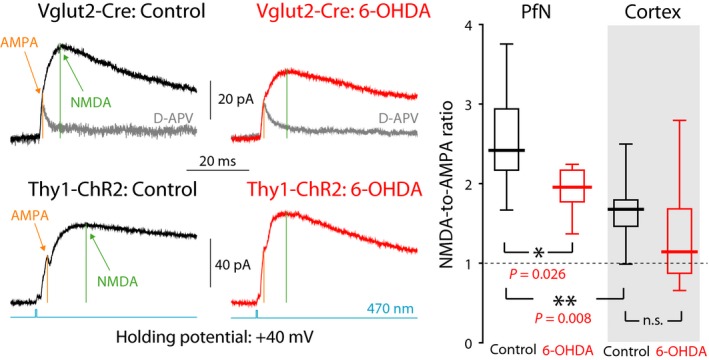
NMDA currents are relatively larger for PfN than for cortical input to ChIs and are reduced at PfN synapses onto ChIs following dopamine depletion. Left: Averaged optogenetic EPSC evoked in ChIs clamped at +40 mV due to PfN input in a control Vglut2‐Cre mouse (top, left), and in a 6‐OHDA‐lesioned Vglut2‐Cre mouse (top, right); nominally cortical input in a control Thy1‐ChR2 mouse (bottom, left), and in a 6‐OHDA‐lesioned Thy1‐ChR2 mouse (bottom, right). Light gray traces are the responses after application of D‐APV, an NMDAR antagonist. Right: Boxplots of NMDA‐to‐AMPA ratios at cortical and PfN synapses in control mice, and 6‐OHDA‐lesioned mice, reveal that the NMDA component at PfN synapses is significantly larger than at cortical synapses onto ChIs and is reduced following 6‐OHDA lesions. n.s.—not significant.
