Figure 3.
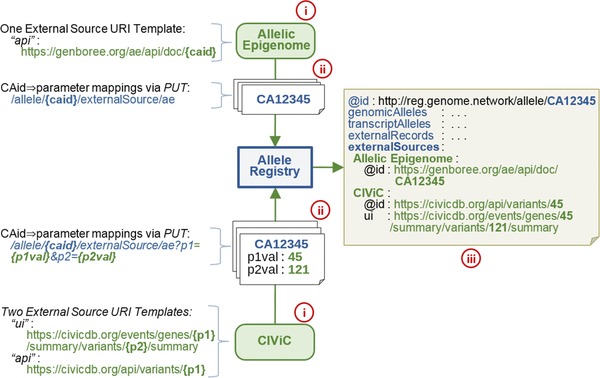
Registry API services permit on‐demand linking of variant information from external sources. (i) The external source indicates their RFC6570 URI template for their API and, optionally, for their UI. (ii) Then the external source associates one or more parameters with CAids about which they have information via PUT requests to the Registry API. Bulk uploads of associations are also supported. These parameters will be used to fill the templates, thereby creating the appropriate link. (iii) The Registry can now include links to these external sources in addition to its own core variant metadata. For the Allelic Epigenome case, because their API directly employs CAids, no parameter values need be supplied when registering a link via the PUT requests to the Registry. In contrast, if CIViC were to add links from Registry alleles to their data, two parameter values (p1, p2) would be registered for each CAid. Based on the CIViC templates shown, both parameter values are needed to construct the appropriate web page URL, whereas only one is needed to form the CIViC “api” URL
