Table 1.
Optimization of 4-Me-Anilide-Substituted Electrophile: Effect of Ligand
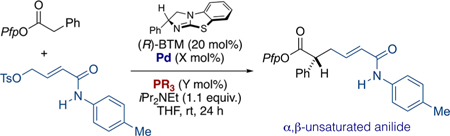 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entrya | Pd(mol%) | PR3(mol%) | Yield[%]b | E:Zc | erd |
| 1 | PdXantphos G3 | -- | 40 | 2.3:1 | 96.4 |
| 2 | Pd2dba3(5) | Xantphos (10) | 56 | 2.5:1 | 95.5 |
| 3 | Pd2dba3(5) | DPEphos (10) | 40 | 3:1 | 96.4 |
| 4 | Pd2dba3(5) | dppf (10) | 37 | 2.1:1 | 95.5 |
| 5 | Pd2dba3(5) | dppe (10) | 26 | 1.9:1 | 96.4 |
| 6 | Pd2dba3(5) | PCy3 (20) | 0 | -- | -- |
| 7 | Pd2dba3(5) | P(o-tolyl)3 (20) | 0 | -- | -- |
| 8 | Pd2dba3(5) | P(4-OMePh)3 (20) | 28 | 2.5:1 | 94.6 |
| 9 | Pd2dba3(5) | P(2-furyl)3 (20) | 15 | 100:1 | 92.8 |
| 10 | Pd2dba3(5) | P(2-thienyl)3 (20) | 43 | 6.6:1 | 96.4 |
| 11 | Pd2dba3(5) | P(2-thienyl)3 (10) | 85 | 7.2:1 | 94.6 |
| 12 | Pd2dba3 (10) | P(2-thienyl)3 (25) | 90 | 7.9:1 | 96.4 |
Reactions performed on a 0.1 mmol scale.
Yields determined by 1H NMR by comparison with an internal standard (1,2,4,5-tetramethylbenzene).
E/Z ratio calculated from crude 1H NMR.
Determined by chiral HPLC analysis.
