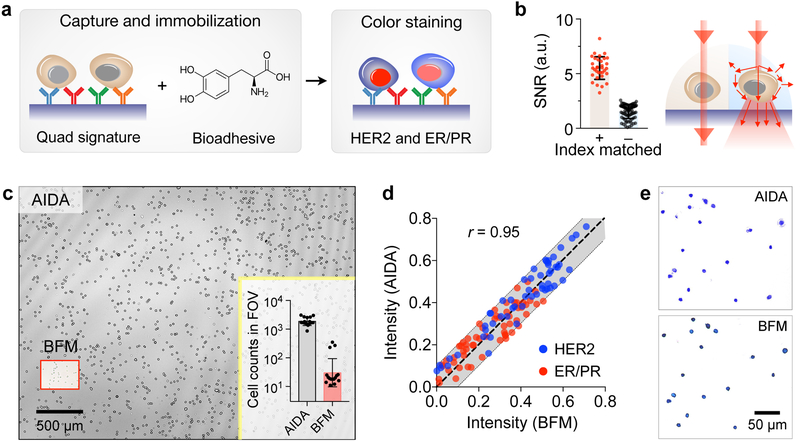
Fig. 2. Assay development.
(a) Cell capture and staining. Immunolabeled cancer cells are captured on a glass surface conjugated with a cocktail of antibodies against EpCAM, EGFR, HER2, and MUC1. Capture cells are further immobilized by applying a 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA)-based bioadhesive. Cells are then immunostained for ER/PR and HER2 expression. (b) Applying index-matching solution to the samples improved the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) more than 3-fold compared to using PBS buffer. (c) Field of view (FOV) comparison between AIDA and bright-field microscopy (BFM). The entire FOV of AIDA was ~25 mm2, about 100 times larger than the FOV of conventional BFM (a 20× objective). In one example (inset), AIDA imaged ~2,000 cells per acquisition, whereas the imaged cell numbers with BFM were ~60 cells. (d) The AIDA signals strongly correlated with those measured by BFM (Pearson correlation coefficient r = 0.95). (e) Comparison between BFM image and pseudo-colored reconstruction image from AIDA.